|
|
|
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Fatal fungal infections may be able to resist newer antifungal drugs. Globally, fungal infections are often fatal due to the lack of access to multiple antifungals, which may be required to be utilized in combination. Single antifungals may not be enough to stop a fungal infection from causing the death of a patient.
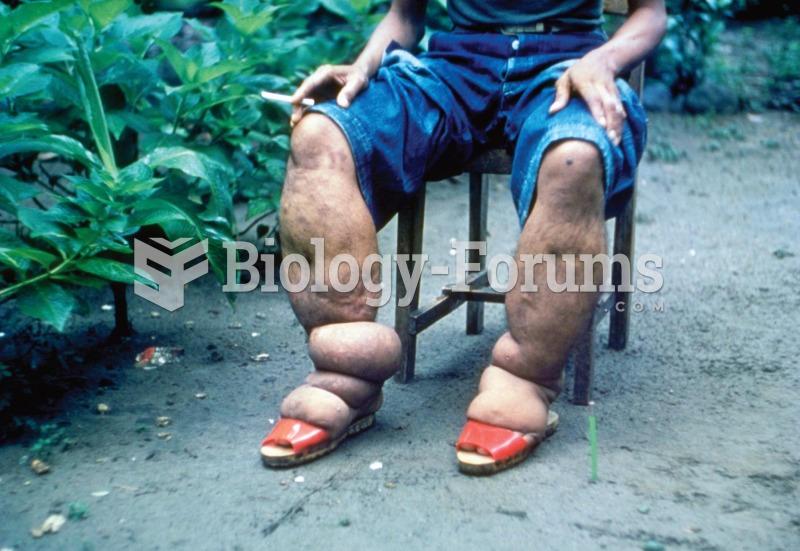
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.