It's "principal" quantum numbers, but OK.
You can't figure it out because it's a dumb question, the point of which is useless trivia rather than actual understanding or application of chemical principles. (Which isn't "principals".) Whoever asked it of you is a silly person who is missing the point.
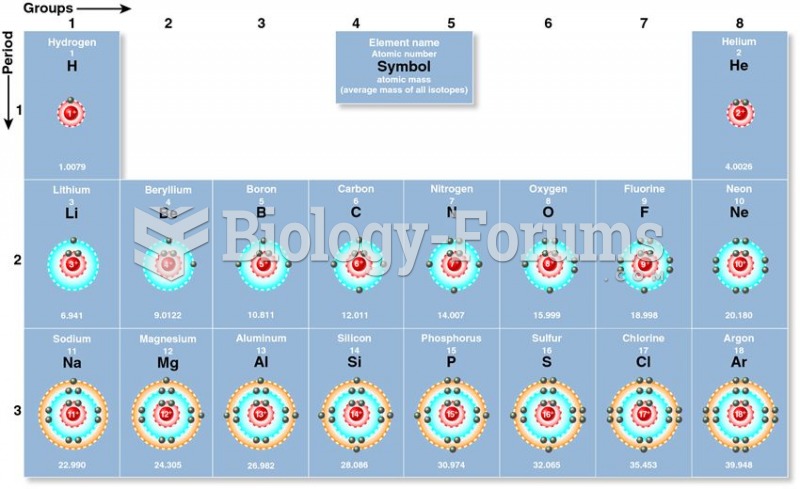
You are absolutely correct. Same group = same # valence electrons = same valence electronic config = same chemistry. That's the take home message, that's the reason to learn electronic configs, that's the reason the periodic table is so astoundingly useful. You got that message, you're in good shape.
Except that the configs on the table are those determined by experimental measurements of gas phase atoms. And sometimes, especially when different subshells in different shells have similar energies, you can get expt'l gas phase configs that do not correspond to Aufbau predictions.
In other words, the d- and f-flock sometimes act goofy, because 6s and 5d and 4f are all similar energies, so that electrons can sometimes hop among them in ways you didn't expect and cannot predict. Which means that the "same valence electronic config" part doesn't always work perfectly.
None of which reduces the utility of the exercise, or the validity of the principle, because YOU DON'T CARE. Well, you care if you do chemistry with gas phase transitional metal atoms, but that's unlikely. You don't care that Cr is [Ar](4s1)(3d5) and not [Ar](4s2)(3d4), because both configs tell you the same thing: 6 valence electrons to play with, +6 is max oxidation state, just like Mo and W. They all become the same once you form an ion in a molecule, so gas phase atoms tomfoolery is irrelevant.
Your answer is Ni Pd Pt. In the gas phase, Ni is (4s2)(3d8), Pd is (4d10), Pt is (6s1)(5d9). There is no possible way to know that or figure that out except to squint at the table. And it's a useless thing to know, unless you're a gas-phase transition-metal chemist (in which case it's super useful to know). For most of us, Ni Pd Pt are all in Group 10, so they all have ten valence electrons, they all form d8 +2 ions, they have similar chemistry and form similar compounds.