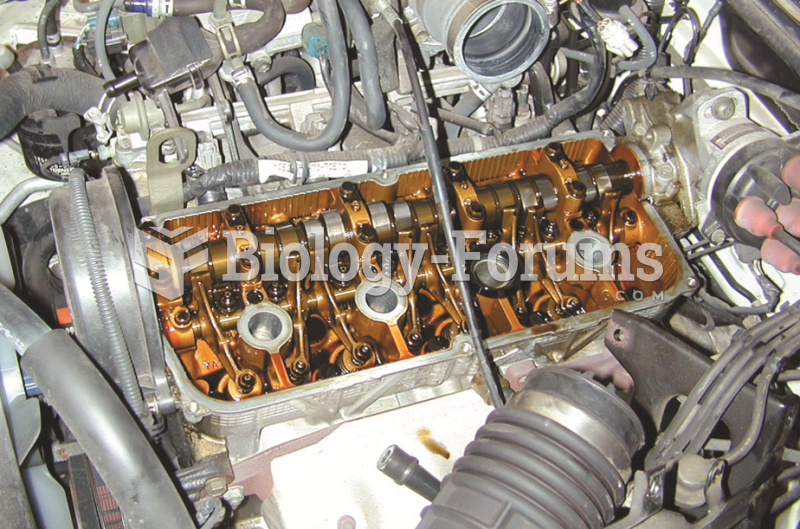
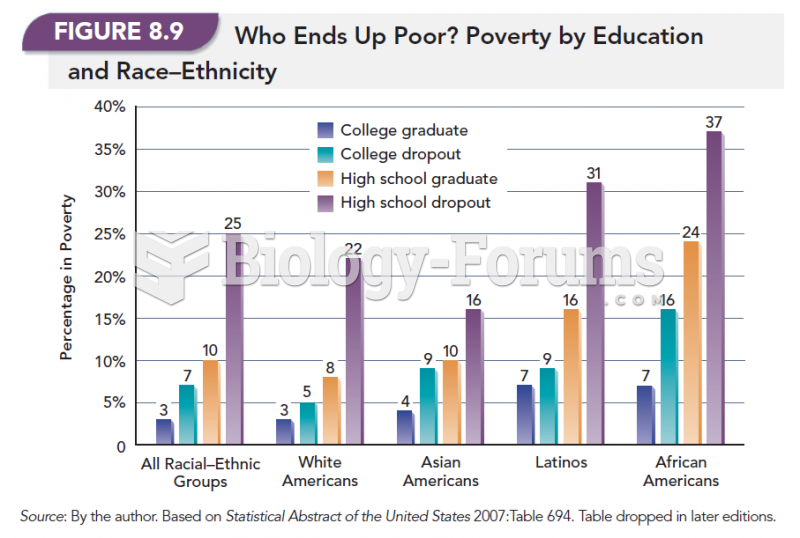
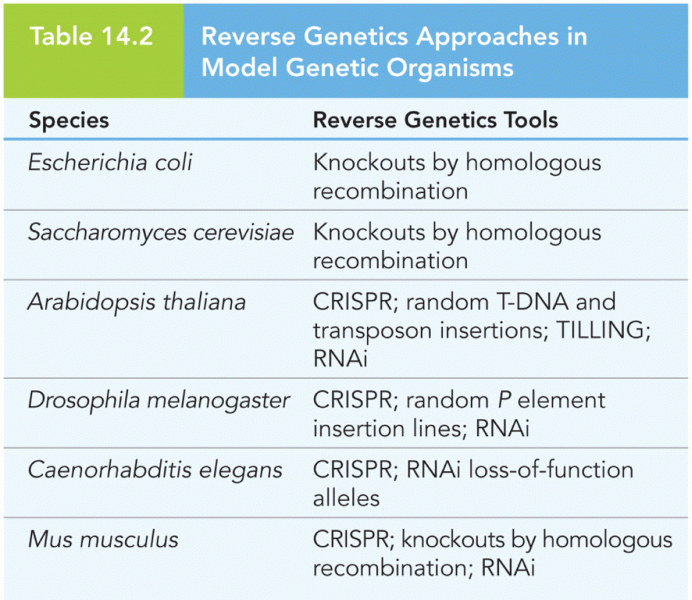
Answer to Question 1
Transition programs teach children either entirely or partly in their native language (depending on their proficiency in English) so they don't fall behind academically while they are learning English. But once they have a working knowledge of English, all instruction is given in English. Some transition programs include an ESL (English as a second language) component to minimize the amount of time instruction must be given in the native language.
Maintenance programs provide instruction in the student's native language for a longer period of time than is the case with transition programs before transitioning to English. The rationale is that a solid foundation in one's native language supports the learning of both English and subject matter knowledge and strengthens the student's cultural identity.
Two-way bilingual programs provide classroom instruction in two languages to all students. For some students one of the two languages is their primary language while the other language is primary for the other students. For example, the primary language for some children in the Canadian province of Qubec is French while for others it is English. Similarly, the primary language for some children in Miami, Florida, is Spanish while for others it is English. Two-way programs typically begin in kindergarten or the primary grades and last for several years. At the end of that time all students are equally proficient in both languages.
All three programs have the same goal: to help minority-language students acquire the English skills they will need to succeed in school and society. They differ in how much time they devote to instruction in the student's native language. Transition programs spend the least amount of time teaching in the student's native language because English is the principal medium through which instruction is delivered and people converse in society at large. Two-way programs spend the greatest amount of time delivering instruction in the student's primary language because language is viewed as an important aspect of culture and strengthening students' cultural identity is considered to have motivational value.
Answer to Question 2
D