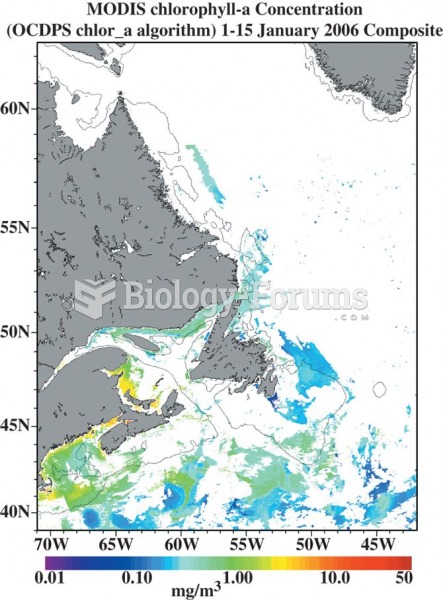
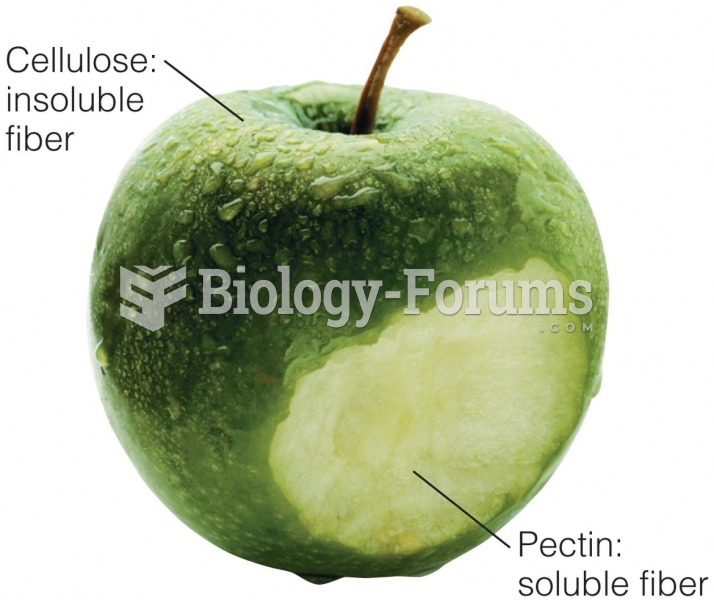
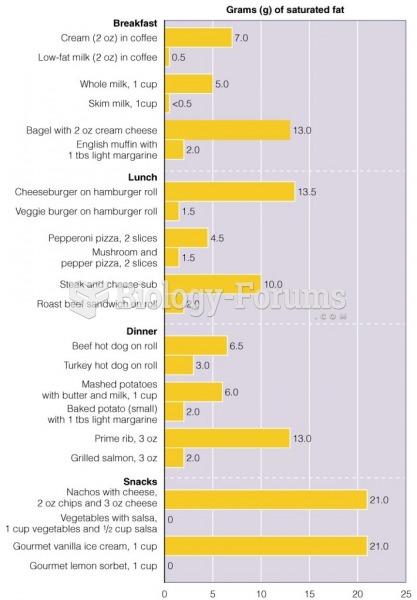
|
|
|
The term bacteria was devised in the 19th century by German biologist Ferdinand Cohn. He based it on the Greek word "bakterion" meaning a small rod or staff. Cohn is considered to be the father of modern bacteriology.
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
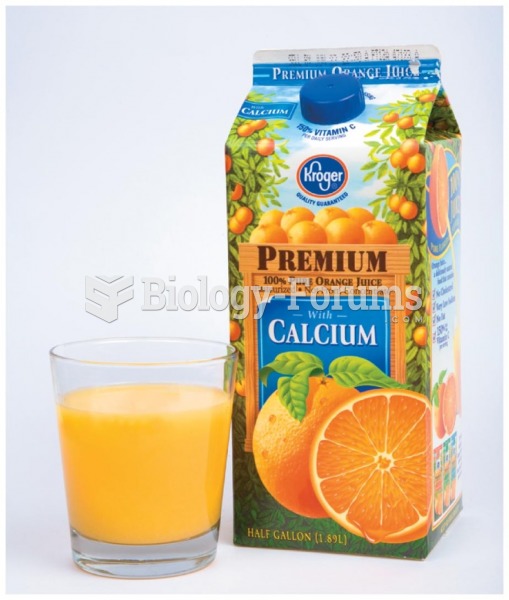
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.
In the United States, congenital cytomegalovirus causes one child to become disabled almost every hour. CMV is the leading preventable viral cause of development disability in newborns. These disabilities include hearing or vision loss, and cerebral palsy.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.