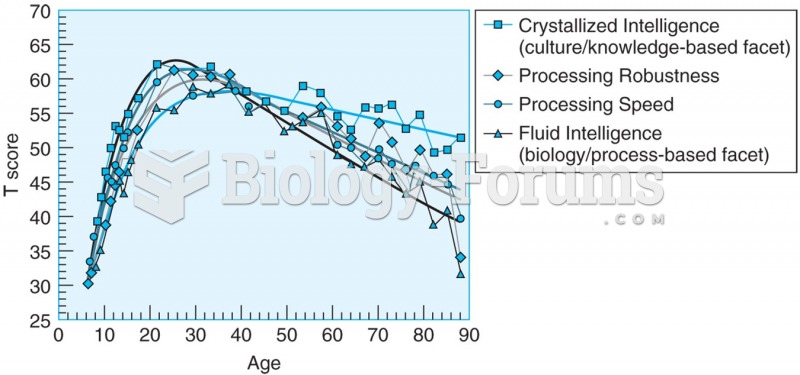
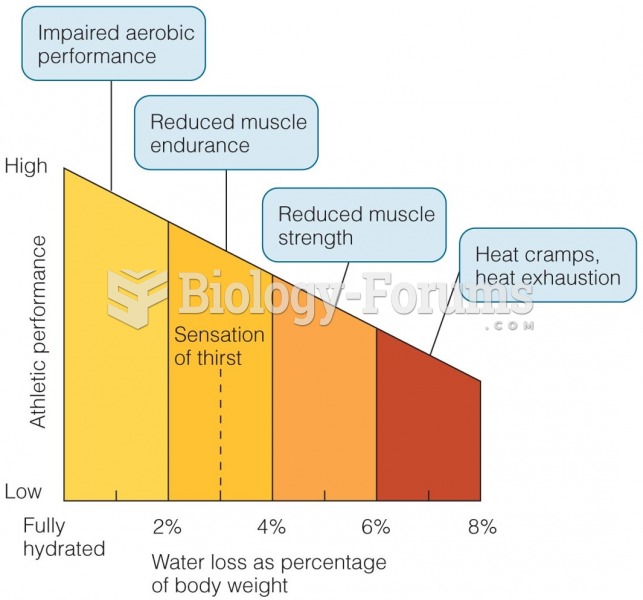
Answer to Question 1
Answer: This case gives students experience using the chapter's diagnostic models to identify motivation and performance problems. The following performance problems, supporting evidence, and recommended actions are an important part of answering the questions. Given the following information, students should provide specific examples from the case of ways in which satisfaction and performance interact for particular individuals. The best responses will indicate that satisfaction often is a result of performance, rather than vice-versa.
Performance Problems
1. Inadequate resources
2. Expectations not understood
3. Rewards not linked to performance
4. Tasks have low identity and feedback
5. Performance not linked to salient rewards
6. Inequity
7. Lack of training
8. Possible placement mismatch
Supporting Evidence (numbers correspond with preceding)
1. Pat: Staff being shifted to other projects
2. Bob: Boss too busy to discuss goals/priorities
3. Chris: Senior members get preference for staff, salary.
4. Chris: Do not understand contribution. Do not receive feedback.
5. Meg: Administrative staff do not receive respect.
Chris: Lack of recognition and appreciation
P.J.: Feeling pressure to advance
Engineers with most responsibility and authority tend to leave.
6. Chalida: Doing work of engineers, receiving pay of tech
7. Meg: Needs administrative education
8. Meg: History majorassistant head of administration
Recommended Actions (numbers correspond with preceding)
1. More frequent planning/coordination meetings. Possibly more staffpossibly hire part-time students from local university during peak periods.
2. More frequent staff meetings. Upper management review first level managers' unit plans and expectations.
3. Set up a formal salary and benefits program.
4. Redesign some jobs by combining tasks, building relationships with client groups.
5. Steve model behavior by spending more time in the administration unit.
6. Adjust unrealistic expectations. Provide opportunities for continuing education.
7. Follow the retrain, refit, reassign approach.
8. Same as 7.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: This case gives students experience using the chapter's diagnostic models to identify motivation and performance problems. The following performance problems, supporting evidence, and recommended actions are an important part of answering the questions. Given the following information, students should provide examples of individuals who are exhibiting low motivation.
Performance Problems
1. Inadequate resources
2. Expectations not understood
3. Rewards not linked to performance
4. Tasks have low identity and feedback
5. Performance not linked to salient rewards
6. Inequity
7. Lack of training
8. Possible placement mismatch
Supporting Evidence (numbers correspond with preceding)
1. Pat: Staff being shifted to other projects
2. Bob: Boss too busy to discuss goals/priorities
3. Chris: Senior members get preference for staff, salary.
4. Chris: Do not understand contribution. Do not receive feedback.
5. Meg: Administrative staff do not receive respect.
Chris: Lack of recognition and appreciation
P.J.: Feeling pressure to advance
Engineers with most responsibility and authority tend to leave.
6. Chalida: Doing work of engineers, receiving pay of tech
7. Meg: Needs administrative education
8. Meg: History majorassistant head of administration
Recommended Actions (numbers correspond with preceding)
1. More frequent planning/coordination meetings. Possibly more staffpossibly hire part-time students from local university during peak periods.
2. More frequent staff meetings. Upper management review first level managers' unit plans and expectations.
3. Set up a formal salary and benefits program.
4. Redesign some jobs by combining tasks, building relationships with client groups.
5. Steve model behavior by spending more time in the administration unit.
6. Adjust unrealistic expectations. Provide opportunities for continuing education.
7. Follow the retrain, refit, reassign approach.
8. Same as 7.