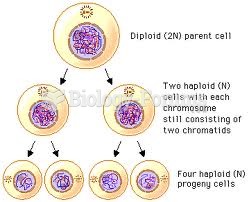
Answer to Question 1
D
Answer to Question 2
Answer: The calm waters view of organizational change envisions the organization as a large ship crossing a calm sea. The ship's captain and crew know exactly where they are going because they have made the trip many times before. Change comes in the form of an occasional storm, a brief distraction in an otherwise calm and predictable trip. In the calm waters metaphor, change is seen as an occasional disruption in the normal flow of events.
It is best illustrated by Kurt Lewin's three-step description of the change process.
According to Lewin, successful change can be planned and requires unfreezing the status quo, changing to a new state, and refreezing to make the change permanent. The status quo can be considered an equilibrium state. To move from this equilibrium, unfreezing is necessary. Unfreezing can be thought of as preparing for the needed change. It can be achieved by increasing the driving forces, which are forces pushing for change; by decreasing the restraining forces, which are forces that resist change and push behavior toward the status quo; or by combining the two approaches.
Once unfreezing is done, the change itself can be implemented. However, merely introducing
change does not ensure that it will take hold. The new situation needs to be refrozen so that it can be sustained over time. Unless this last step is done, there is a strong chance that employees will revert back to the old ways of doing things. The objective of refreezing, then, is to stabilize the new situation by reinforcing the new behaviors.
Lewin's three-step process treats change as a move away from the organization's current equilibrium state. It is a calm waters scenario where an occasional disruption means changing to deal with the disruption. Once the disruption has been dealt with, however, things can continue on under the new changed situation.