|
|
|
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.
Many people have small pouches in their colons that bulge outward through weak spots. Each pouch is called a diverticulum. About 10% of Americans older than age 40 years have diverticulosis, which, when the pouches become infected or inflamed, is called diverticulitis. The main cause of diverticular disease is a low-fiber diet.
Serum cholesterol testing in adults is recommended every 1 to 5 years. People with diabetes and a family history of high cholesterol should be tested even more frequently.
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
The use of salicylates dates back 2,500 years to Hippocrates's recommendation of willow bark (from which a salicylate is derived) as an aid to the pains of childbirth. However, overdosage of salicylates can harm body fluids, electrolytes, the CNS, the GI tract, the ears, the lungs, the blood, the liver, and the kidneys and cause coma or death.
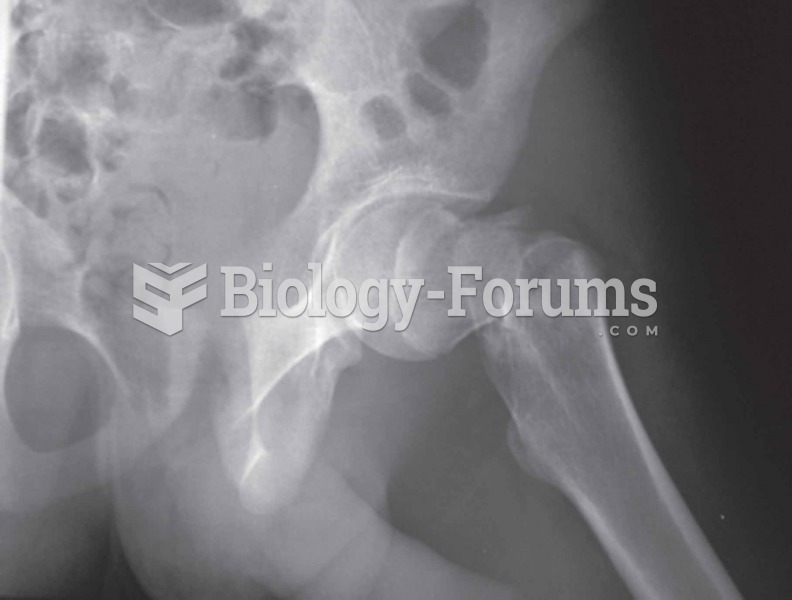 Hip Typically occurs as a result of a fall; with osteoporosis, hip fractures can occur as a result o
Hip Typically occurs as a result of a fall; with osteoporosis, hip fractures can occur as a result o
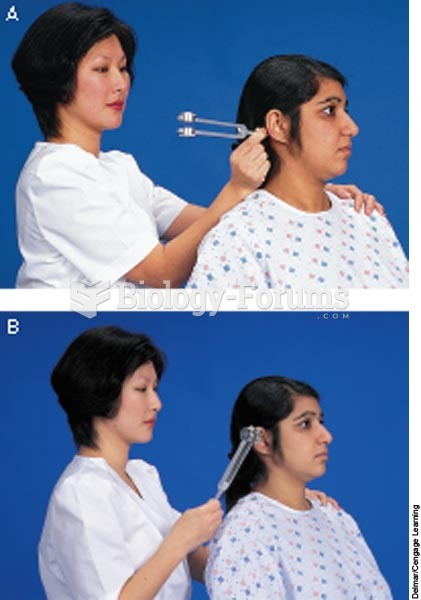 Rinne test: A. Place the base of the tuning fork on the mastoid process. B. Place tuning fork in fro
Rinne test: A. Place the base of the tuning fork on the mastoid process. B. Place tuning fork in fro
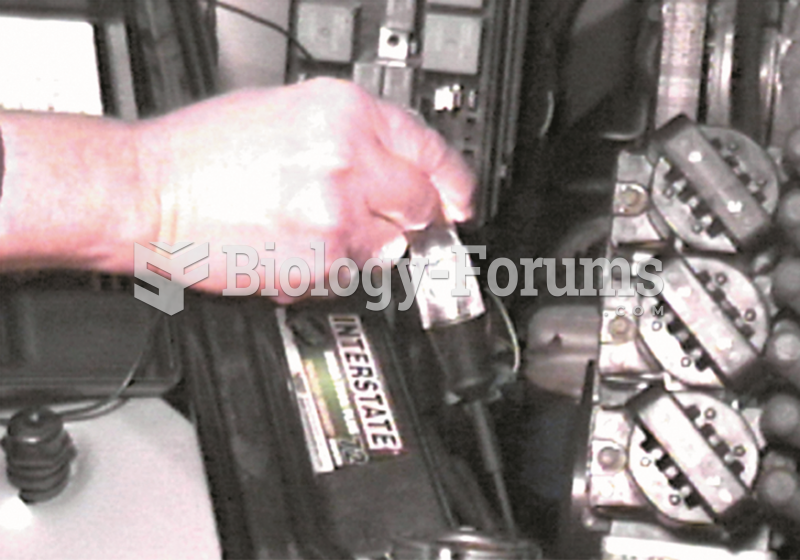 Touch the test light to the negative (–) terminal of the battery or a good engine ground to check ...
Touch the test light to the negative (–) terminal of the battery or a good engine ground to check ...