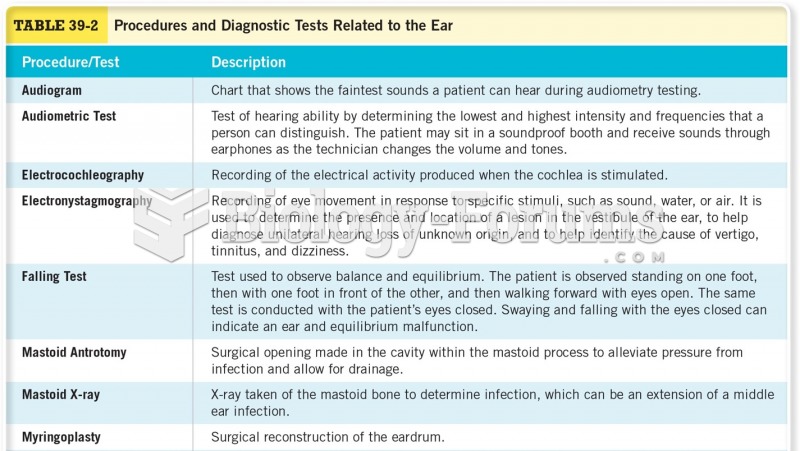
Answer to Question 1
Answer: FALSE
Answer to Question 2
a. Differences in National PreferencesAdaptati on may be carried out to modify the offering to the specific, unique wants and needs of customers in individual markets. When The Simpsons cartoon series was broadcast in Saudi Arabia, it was renamed Al Shamshoon, Homer Simpson's name was changed to Omar, and Bart Simpson became Badr. Producers translated the show into Arabic and modified the way the Simpson daughter and mother dress. Producers removed references to practices considered potentially offensive, such as consuming pork and beer. They changed Homer Simpson's Duff beer to soda, hot dogs to Egyptian beef sausages, and donuts to the popular Arab cookies called kahk.
b. Differences in Living Standards and Economic ConditionsBecause income levels vary substantially around the world, firms typically adjust both the pricing and the complexity of their product offerings for individual markets. For example, Microsoft has had to lower the price of its software for some markets (e.g., Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia) in order to bring them in line with local purchasing power. A recession signals a drop in consumer confidence and the firm may need to reduce prices to generate sales. High inflation can rapidly erode profits even as prices rise.
c. Differences in Laws and RegulationsGermany, Norway, and Switzerland are among countries that restrict advertising directed at children. Packaged foods in Europe are often labeled in several languages, including English, French, German, and Spanish. In Quebec, Canada's French-speaking province, local law requires product packaging to be in the French language.
d. Differences in National InfrastructureInfra structure is especially poor in the rural parts of developing economies, necessitating innovative approaches for getting products to customers. Road and rail networks in western China are underdeveloped, so firms use small trucks to reach retailers in outlying communities. Undeveloped media also require substantial adaptations to carry marketing communications. In rural Vietnam, most consumers cannot access television, magazines, or the Internet. Firms advertise to low-income buyers via radio, billboards, and brochures.