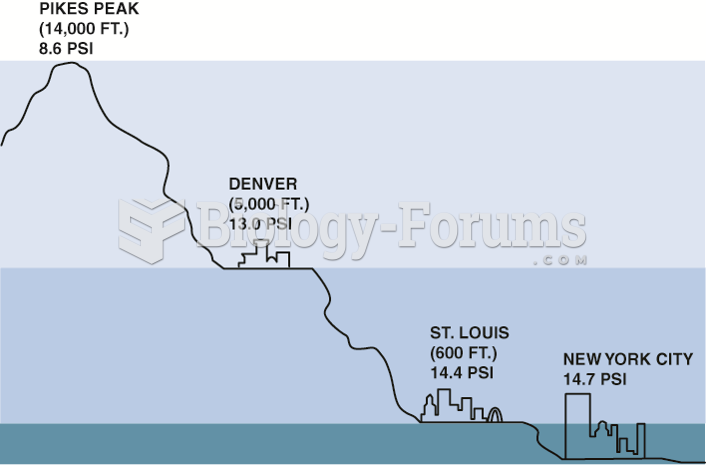
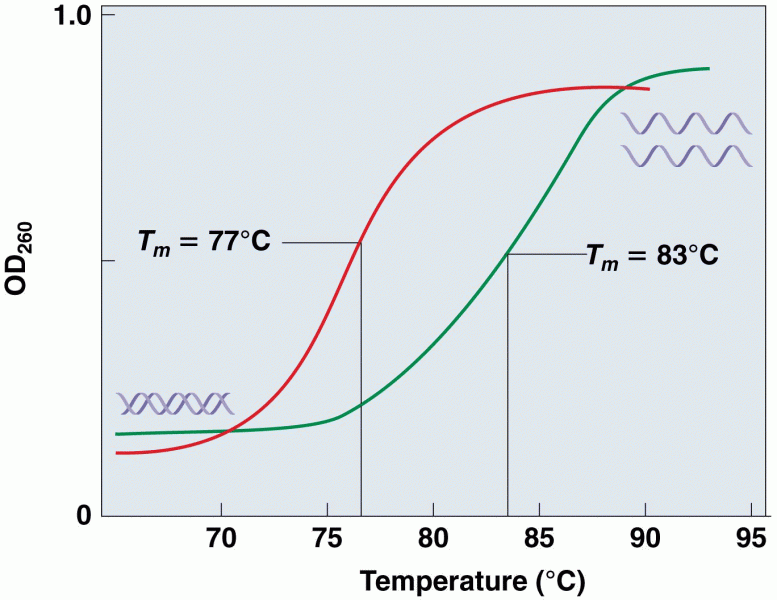
Answer to Question 1
a. Be tolerant of cultural differencesThe partners may never arrive at a common set of values and organizational routines, especially if they're from very distinct culturessay, Norway and Nigeria. But establishing compatibility is important despite cultural differences.
b. Pursue common goalsJapanese firms tend to value market share over profitability, while U.S. firms value profitability over market share. Because different strategies are required to maximize each of these performance goals, a joint venture between Japanese and U.S. firms may fail. To overcome such challenges, partners need to regularly interact and communicate at three levels of the organization: senior management, operational management, and the workforce.
c. Give due attention to planning and management of the ventureWithout agreement on questions of management, decision making, and control, each partner may want to control the venture's operations, which can strain the managerial, financial, and technological resources of both. When one of the partners is clearly the driver or the leader in the relationship, there is less likelihood of a stalemate or prolonged negotiations.
d. Safeguard core competenciesCollabo ration takes place between firms that are current or potential competitors. Accordingly, the partners must walk the line between cooperation and competition. For example, for several years, Volkswagen and General Motors succeeded in China by partnering with the Chinese firm, Shanghai Automotive Industry Corporation (SAIC). The Western firms transferred much technology and know-how to the Chinese partner. Having learned much from VW and GM, SAIC is now poised to become a major player in the global automobile industry, and competitor to its original partners.
e. Adjust to shifting environmental circumstancesWhen environmental conditions change, the rationale for a collaborative venture may weaken or disappear. An industry or economic downturn may shift priorities in one or both firms. Cost overruns can make the venture untenable. New government policies or regulations can increase costs or eliminate anticipated benefits. Managers should maintain flexibility to adjust to changing conditions.
Answer to Question 2
C