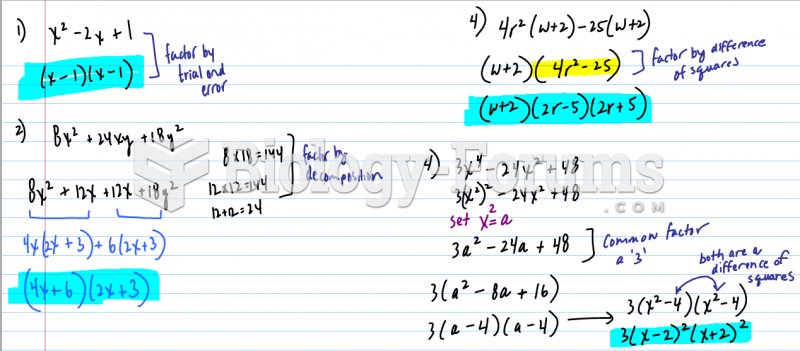
Answer to Question 1
An English economist named David Ricardo developed the theory of comparative advantage in 1817. He proposed that, if one country held absolute advantages in the production of both products, specialization and trade could still benefit both countries. A country has a comparative advantage when it is unable to produce a good more efficiently than other nations but produces the good more efficiently than it does any other good. In other words, trade is still beneficial even if one country is less efficient in the production of two goods, as long as it is less inefficient in the production of one of the goods.
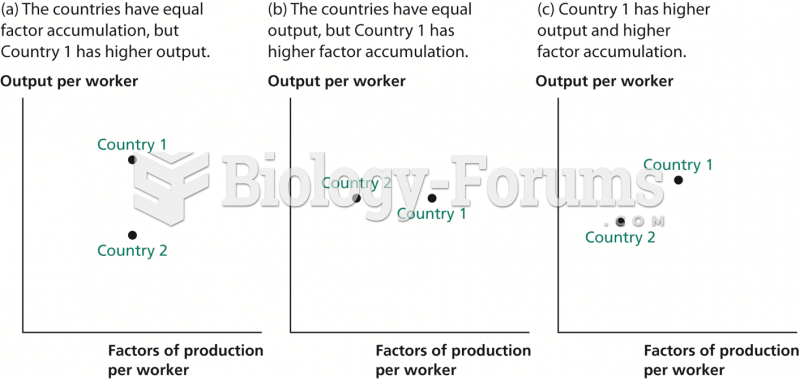
In the early 1900s, an international trade theory emerged that focused attention on the proportion (supply) of resources in a nation. The cost of any resource is simply the result of supply and demand: Factors in great supply relative to demand will be less costly than factors in short supply relative to demand. Factor proportions theory states that countries produce and export goods that require resources (factors) that are abundant and import goods that require resources in short supply. The theory resulted from the research of two economists, Eli Heckscher and Bertil Ohlin, and is therefore sometimes called the HeckscherOhlin theory.
Factor proportions theory differs considerably from the theory of comparative advantage. The theory of comparative advantage states that a country specializes in producing the good that it can produce more efficiently than any other good. Thus, the focus of the theory (and absolute advantage as well) is on the productivity of the production process for a particular good. By contrast, factor proportions theory says that a country specializes in producing and exporting goods using the factors of production that are most abundant and thus cheapest-not the goods in which it is most productive.
Answer to Question 2
B