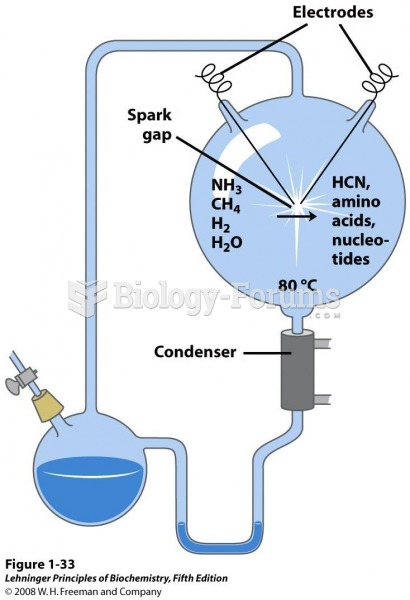
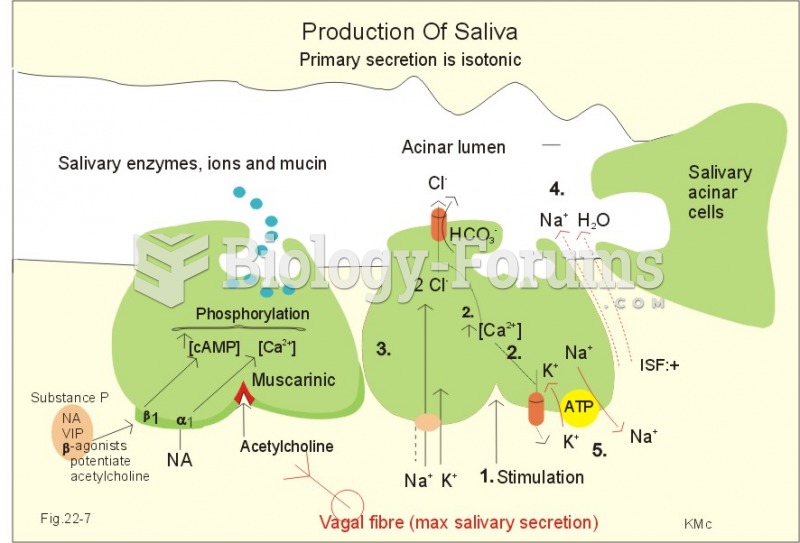
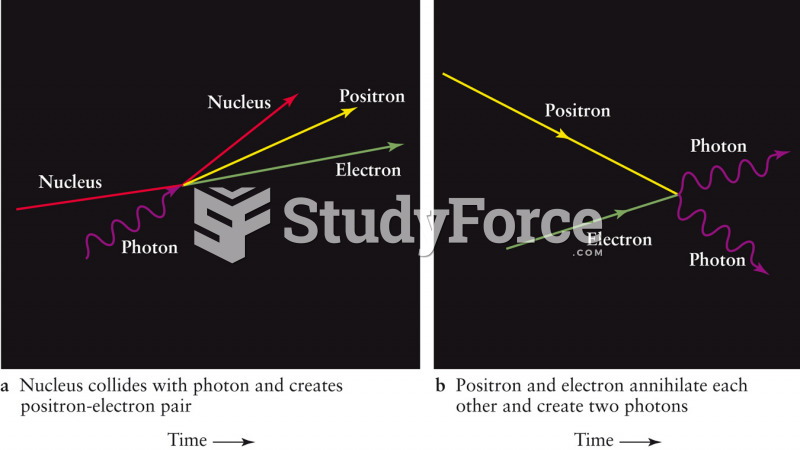
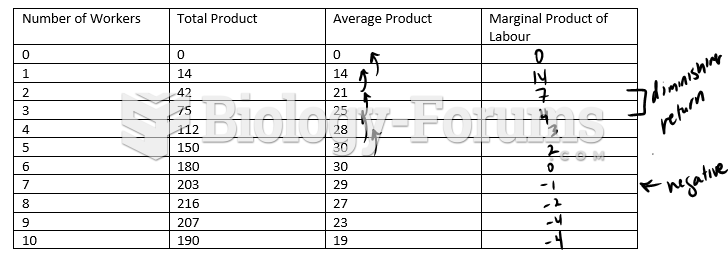
Answer to Question 1
FALSE
Answer to Question 2
Globalization of production refers to the dispersal of production activities to locations that help a company achieve its cost-minimization or quality-maximization objectives for a good or service. This includes the sourcing of key production inputs (such as raw materials or products for assembly) as well as the international outsourcing of services.
Benefits to companies for the globalization of production include:
1. Access to lower-cost workers-Global production activities allow companies to reduce overall production costs through access to low-cost labor. For decades, companies located their factories in low-wage nations to churn out all kinds of goods, including toys, small appliances, inexpensive electronics, and textiles. Yet whereas moving production to low-cost locales traditionally meant production of goods almost exclusively, it increasingly applies to the production of services such as accounting and research. Although most services must be produced where they are consumed, some services can be performed at remote locations where labor costs are lower. Many European and U.S. businesses have moved their customer service and other nonessential operations to places as far away as India to slash costs by as much as 60 percent.
2. Access to technical expertise-Companies also produce goods and services abroad to benefit from technical know-how.
3. Access to production inputs-Globalization of production allows companies to access resources that are unavailable or more costly at home. The quest for natural resources draws many companies into international markets. If a company commits to the globalization of production, its leadership should study international firm management because this management arena is vastly different from managing a purely domestic business. Companies must abide by the rules in every market in which they choose to operate. Therefore, the context of international business management is defined by the characteristics of national business environments. Because of widely dispersed production and marketing activities today, firms commonly interact with people in distant locations within the international business environment. Finally, managers and their firms are compelled to be knowledgeable about the nations in which they operate because of the integrating power of globalization. Businesses should try to anticipate events and forces that can affect their operations by closely monitoring globalization, national business environments, and the international business environment.