|
|
|
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
The first-known contraceptive was crocodile dung, used in Egypt in 2000 BC. Condoms were also reportedly used, made of animal bladders or intestines.
There are over 65,000 known species of protozoa. About 10,000 species are parasitic.
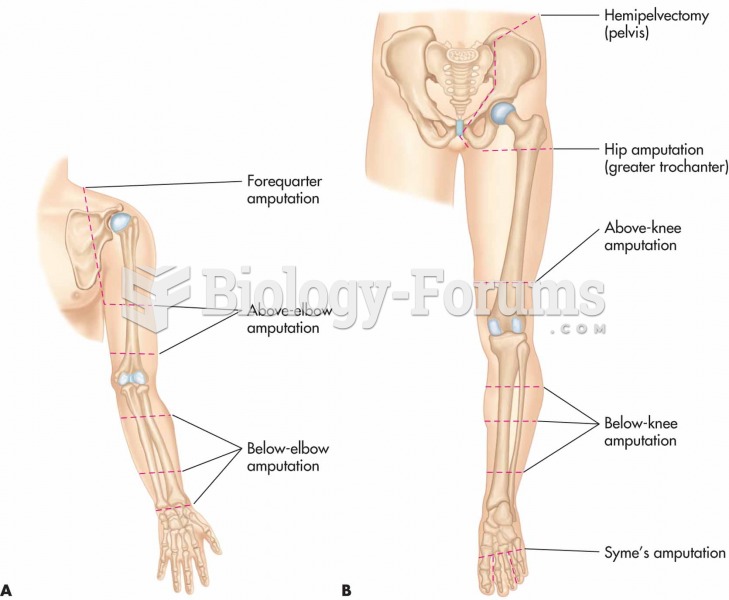
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
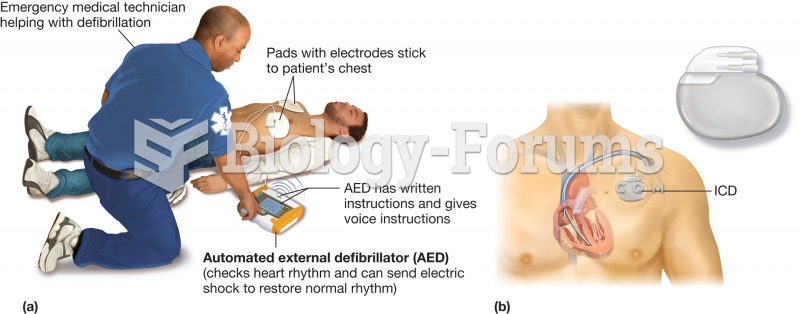 Defibrillator. Defibrillators are devices that supply a voltage charge to the heart in the hope of r
Defibrillator. Defibrillators are devices that supply a voltage charge to the heart in the hope of r
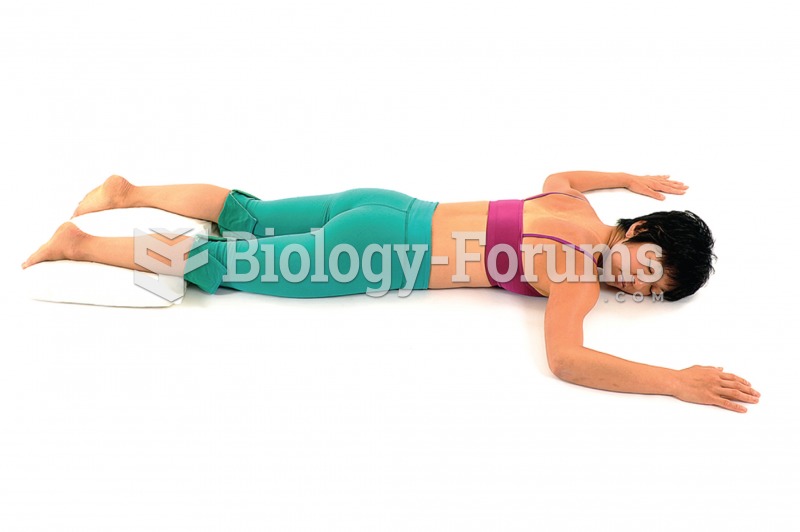 Lie prone with your head turned to one side. Put your arms out to your sides and bend your elbows at ...
Lie prone with your head turned to one side. Put your arms out to your sides and bend your elbows at ...