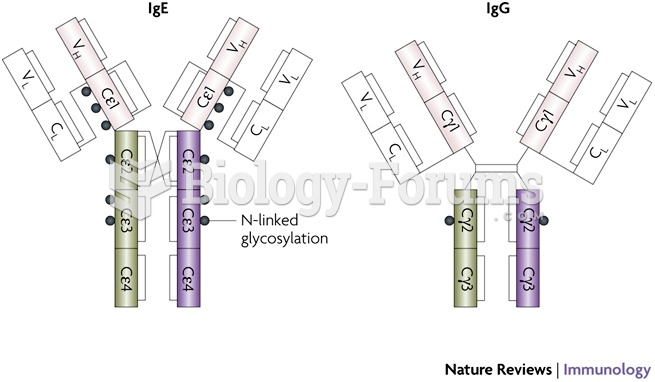
Answer to Question 1
IP addresses can be used instead of URLs to navigate to particular Web addresses. This practice is not done regularly, as IP addresses are far more difficult to remember than domain names, and an organization may assign its domain name to a server with a different IP address. While the IP address behind a domain name may change, the domain name stays the same.
Answer to Question 2
The architecture of the expert system and neural networks can be described using the basic systems model. Inputs to the system are questions and answers from the user. Processing is the matching of user questions and answers to information in the knowledge base. The processing in an expert system is called inferencing, which consists of matching facts and rules, determining the sequence of questions presented to the user, and drawing a conclusion. The output from an ES is a recommendation.
An expert system (ES) is a type of intelligent system that uses reasoning methods based on knowledge about a specific problem domain in order to provide advice, much like a human expert. ESs are used to mimic human expertise by manipulating knowledge-understanding acquired through experience and extensive learning-rather than simply manipulating information. Human knowledge can be represented in an ES by facts and rules about a problem coded in a form that can be manipulated by a computer. When you use an ES, the system asks you a series of questions, much as a human expert would. It continues to ask questions, and each new question is determined by your response to the preceding question. The ES matches the responses with the defined facts and rules until the responses point the system to a solution. A rule is a way of encoding knowledge, such as a recommendation, after collecting information from a user. Rules are typically expressed using an if-then format.
Neural networks, composed of a network of processing elements that work in parallel to complete a task, attempt to approximate the functioning of the human brain and can learn by example. Typically, a neural network is trained by having it categorize a large database of past information for common patterns. Once these patterns are established, new data can be compared to these learned patterns and conclusions drawn.