Answer to Question 1
Mental models are knowledge structures that individuals construct to understand and explain their experiences. The models are constrained by the individuals' implicit theories about these experiences, which can be more or less accurate. Johnson-Laird also hypothesized that individuals use propositions, which he conceptualized as fully-abstracted representations of verbally expressible; and that they use images.
Answer to Question 2
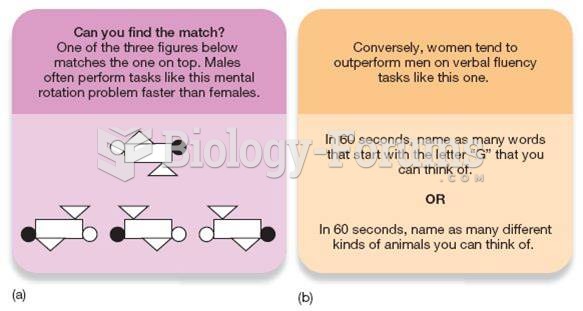
Mental rotation involves rotationally transforming an object's visual mental image (Takano & Okubo, 2003; Zacks, 2008). Just like you can physically rotate a water bottle you hold in your hands, you can also imagine a water bottle in your mind and rotate it in the mind.
Current brain-imaging techniques have allowed researchers to create images of human brain activity noninvasively to address such speculations. For example, in a study using fMRI, investigators found that the same brain areas involved in perception also are involved in mental rotation tasks. In one study, participants physically rotated objects instead of merely watching them being rotated. Later, they imagined the rotation of these objects. Parts of their motor cortex were activated that normally would not have been activated during mental rotation. In other words, the prior physical rotation of the objects affected the way their brains later processed the mental rotations of images of those objects. Of particular importance is the early visual cortex. It is the first area that receives input from the retina when we see an object. The early visual cortex (in particular, areas 17 and 18) is activated during imagery. Furthermore, when area 17 is impaired by means of transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), imagery is compromised as well. In mental rotation, the primary motor cortex is activated when participants imagine manually rotating a stimulus (but not when they imagine a rotation driven by an electric motor). Thus, not only are imagery and perception functionally equivalent in many psychological studies, neuropsychological techniques also verify this equivalence by demonstrating overlapping brain activity.