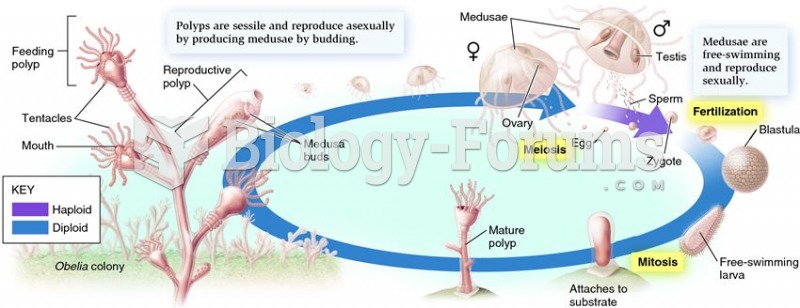
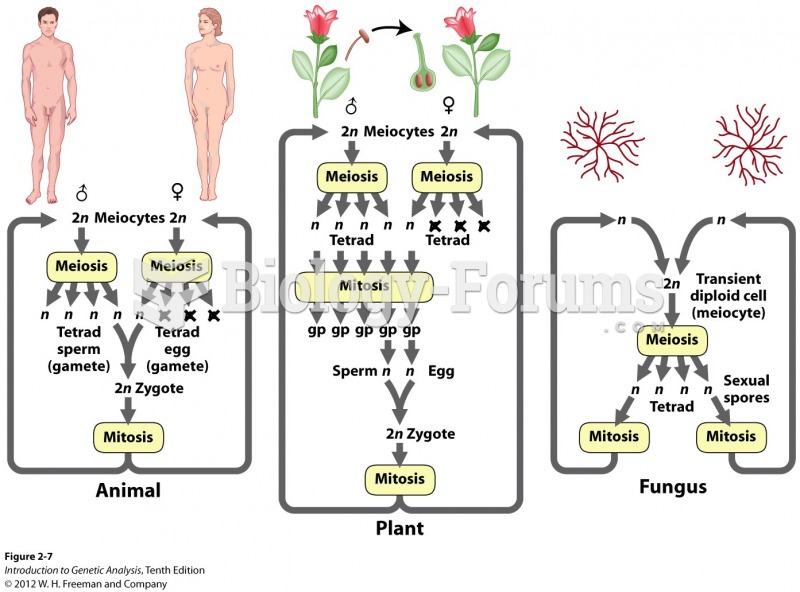
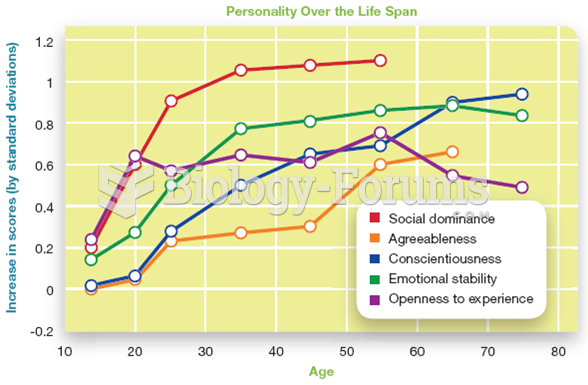
Answer to Question 1
ANS: D
A situational crisis is an unusually stressful life event that exceeds a person's resources and coping skills. Examples include unexpected illness or injury, rape, car accident, loss of home, spouse, job, etc. Erik Erikson's stage model of psychosocial development forms the basis for understanding developmental crises. Each stage is associated with a psychosocial crisis to be resolved. Successful resolution of each maturational stage leaves a person better able to meet the interpersonal challenges and stressors of the next. Examples of critical incidents associated with developmental crises include: marriage, pregnancy and birth of a child, midlife crisis, retirement, meaning in aging, etc. A private crisis affects individuals and families but not the community at large. Examples include suicide, terminal diagnosis, a car crash, rape, or the death of a family member. An adventitious crisis is not a part of everyday experience. It is unplanned, unusual, horrific, and beyond anyone's control. Examples of adventitious crisis include natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, fires, mud slides; national disasters such as terrorism, riots, wars; and crimes of violence such as rape, child abuse, assault, or murder.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: B
Erikson's stage model of psychosocial development forms the basis for understanding developmental crises. Each stage is associated with a psychosocial crisis to be resolved. Successful resolution of each maturational stage leaves a person better able to meet the interpersonal challenges and stressors of the next. Lindemann and Caplan are considered primary contributors to the development of crisis theory. Caplan broadened Lindemann's model to include developmental crisis and personal crisis. Although the direct focus of crisis intervention is on secondary prevention because the crisis state is already in motion, Caplan applied concepts of primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention to crisis intervention. Aguilera developed a nursing model identifying how a crisis develops and corresponding factors needed for resolution. Roberts provides a seven-stage sequential blueprint for clinical intervention, which can be used to structure the crisis intervention process in nurse-client relationships. This model is compatible with the nursing process sequencing of assessment, planning, implementation, and evaluation.