|
|
|
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.
The eye muscles are the most active muscles in the whole body. The external muscles that move the eyes are the strongest muscles in the human body for the job they have to do. They are 100 times more powerful than they need to be.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
Blastomycosis is often misdiagnosed, resulting in tragic outcomes. It is caused by a fungus living in moist soil, in wooded areas of the United States and Canada. If inhaled, the fungus can cause mild breathing problems that may worsen and cause serious illness and even death.
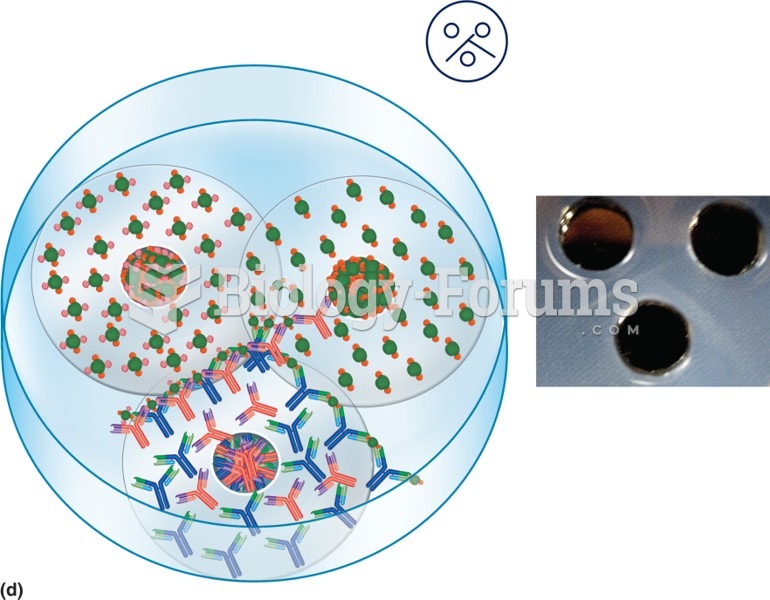 Two wells are filled with related or partially identical antigens. The well on the left contains an ...
Two wells are filled with related or partially identical antigens. The well on the left contains an ...
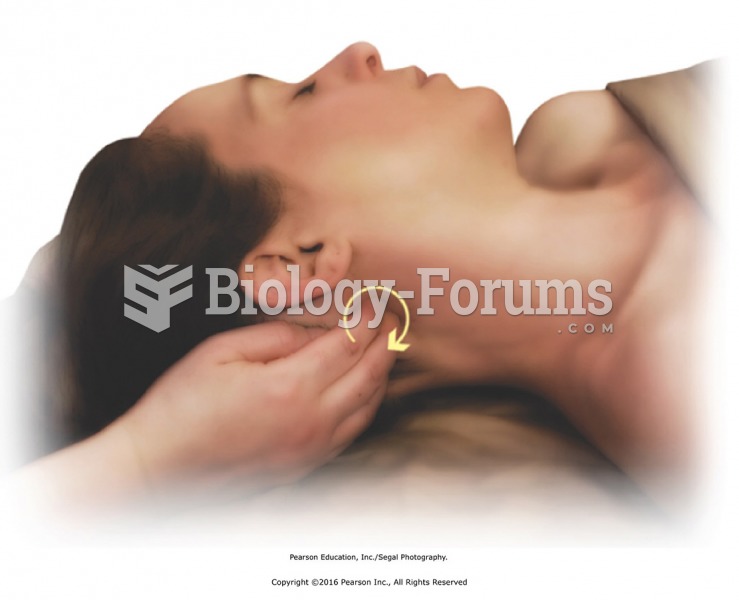
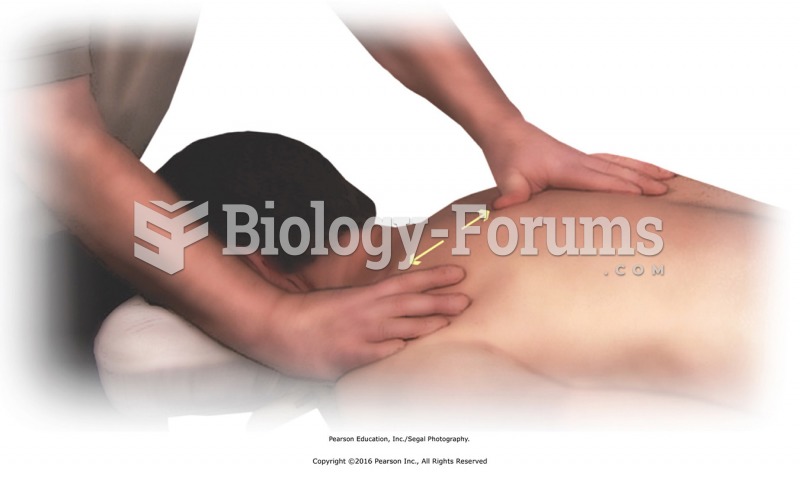
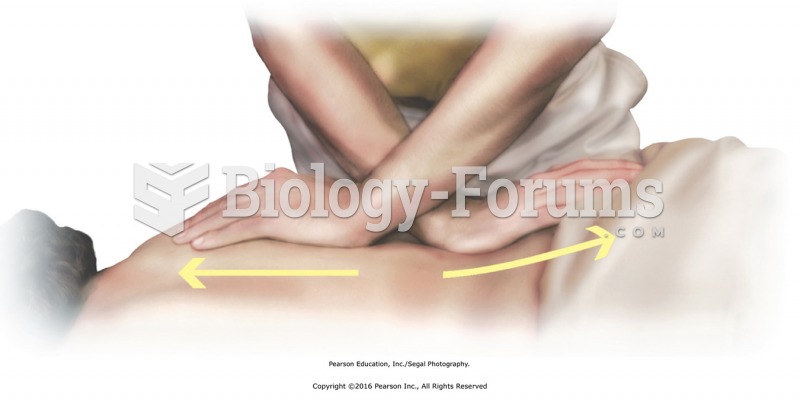 Stand facing the side of the table and apply cross-handed stretches for the subcutaneous fascia. ...
Stand facing the side of the table and apply cross-handed stretches for the subcutaneous fascia. ...