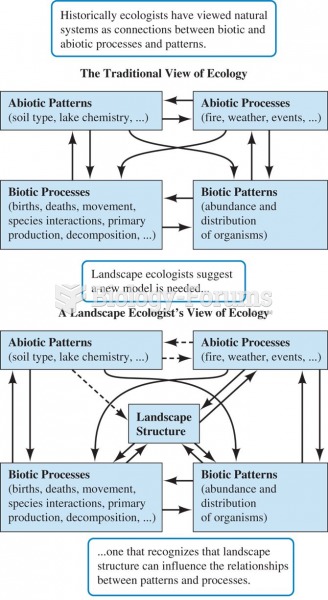
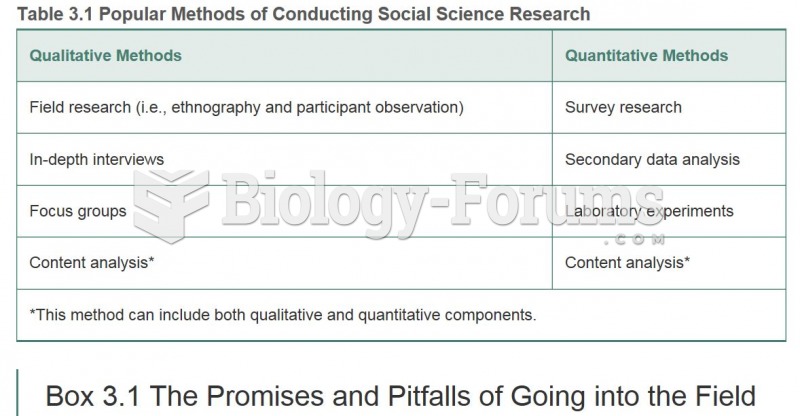
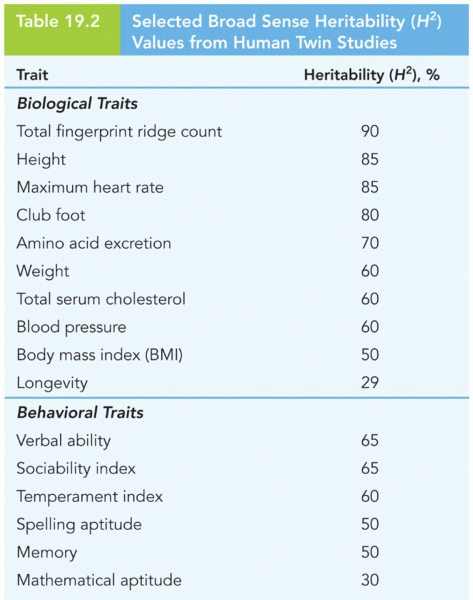
|
|
|
As the western states of America were settled, pioneers often had to drink rancid water from ponds and other sources. This often resulted in chronic diarrhea, causing many cases of dehydration and death that could have been avoided if clean water had been available.
In 2012, nearly 24 milliion Americans, aged 12 and older, had abused an illicit drug, according to the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
Increased intake of vitamin D has been shown to reduce fractures up to 25% in older people.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.