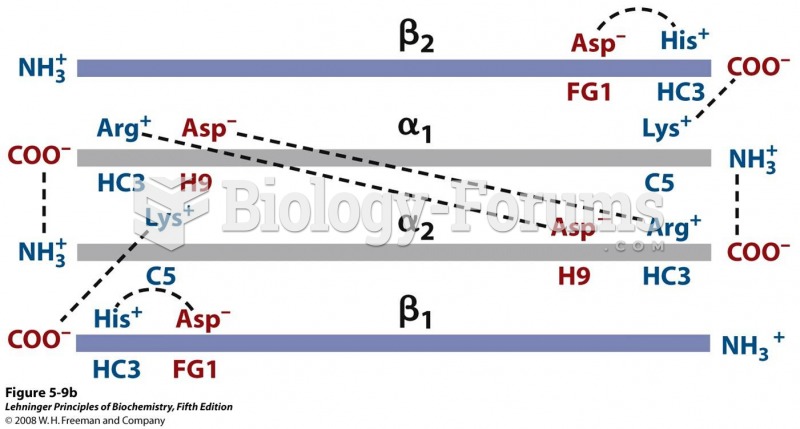
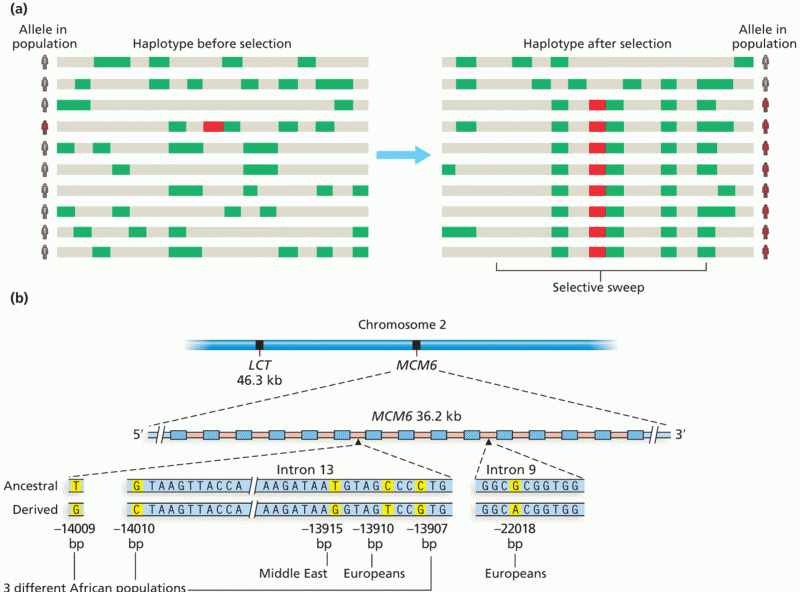
Answer to Question 1
ANS: C
A theory is more narrow and specific than a conceptual model and is directly testable. A theory consists of an integrated set of defined concepts, existence statements, and relational statements that present a view of a phenomenon and can be used to describe, explain, predict, or control that phenomenon. A conceptual model, also known as a grand theory, is a set of highly abstract, related constructs. Scientific theories are those for which repeated studies have validated the relationships among the concepts. Middle-range theories, or substantive theories, present a partial view of nursing reality. These theories are less abstract and address more specific phenomena than grand theories do. They directly apply to practice and focus on explanation and implementation.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: A
Statements about the same two conceptual ideas can be made at various levels of abstractness. The statements found in conceptual models and grand theories (general propositions) are at a high level of abstraction. Statements found in middle range theories (specific propositions) are at a moderate level of abstraction. Hypotheses, which are a form of statement, are at a low level of abstraction and are specific. As statements become less abstract, they become narrower in scope. Statements at varying levels of abstraction that express relationships between or among the same conceptual ideas can be arranged in hierarchical form, from general to specific. This arrangement allows you to see (or evaluate) the logical links among the various levels of abstraction. Statement sets link the relationships expressed in the framework with the hypotheses, research questions, or objectives that guide the methodology of the study. A concept is a term that abstractly describes and names an object, a phenomenon, or an idea, thus providing it with a separate identity or meaning. At high levels of abstraction, concepts have general meanings and are sometimes referred to as constructs. A variable is more specific than a concept and implies that the term is clearly defined and measurable. Hypotheses, which are a form of statement, are at a low level of abstraction and are specific. A theory is more narrow and specific than a conceptual model and is directly testable. A theory consists of an integrated set of defined concepts, existence statements, and relational statements that can be used to describe, explain, predict, or control that phenomenon. The instrument itself is an operational definition of the concept. Operational definitions must be consistent with the conceptual definition and should be accepted methods of measurement used for testing the selected theory.