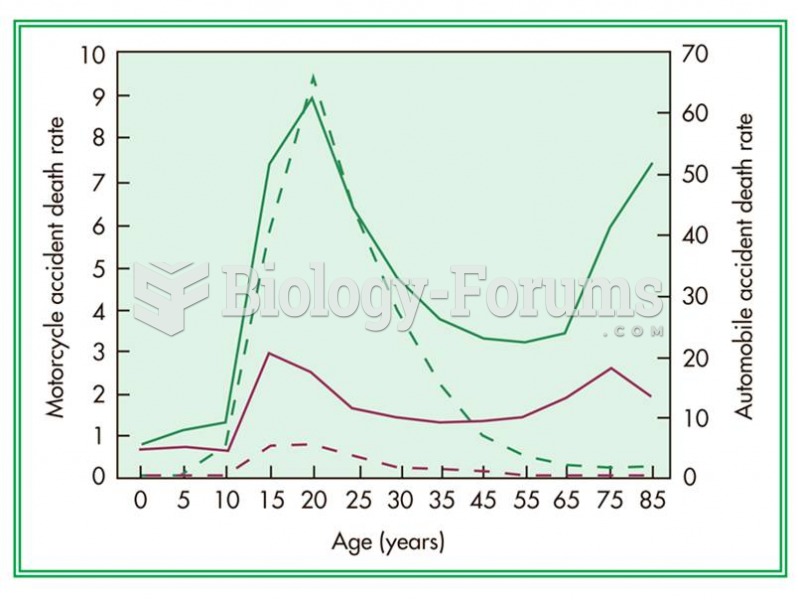
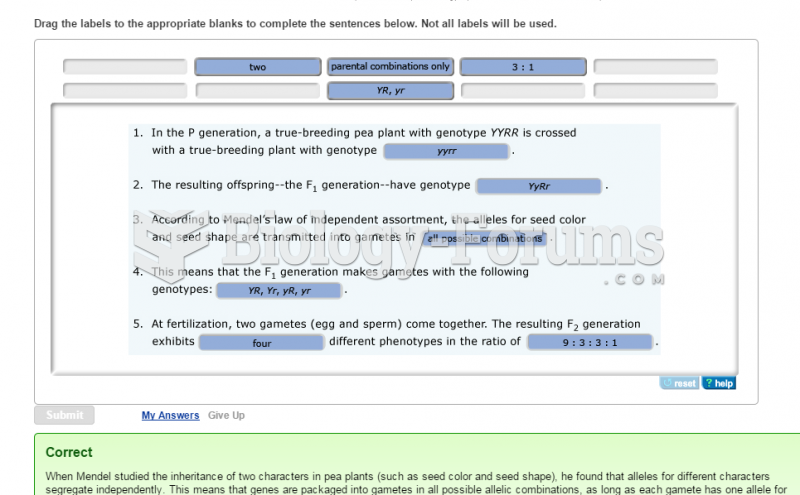
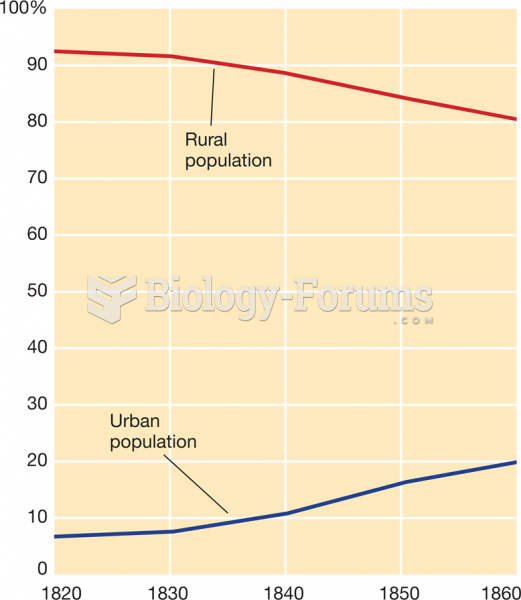
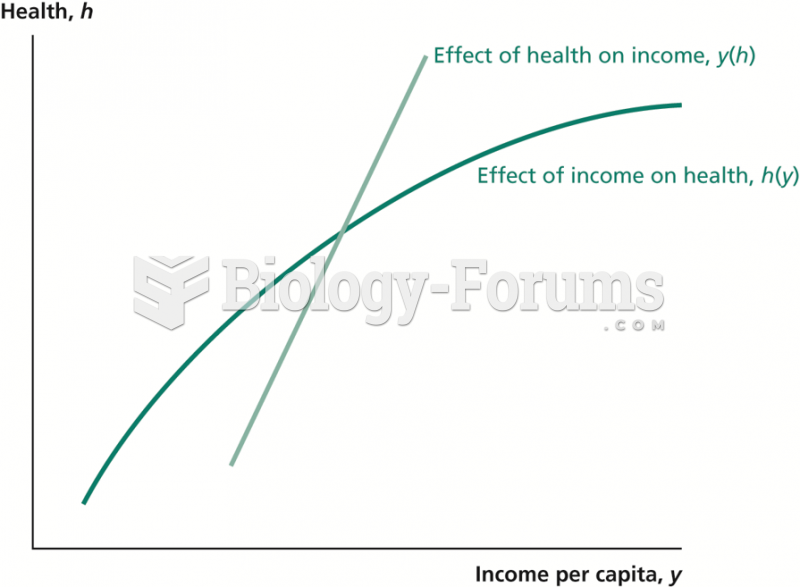
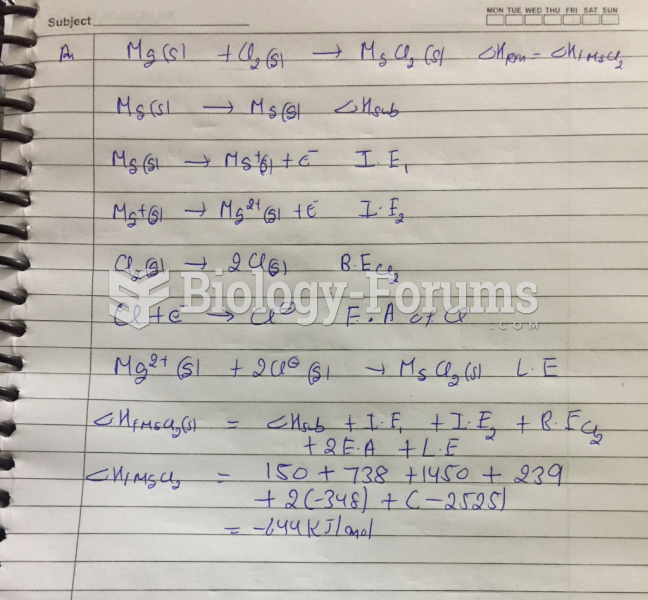
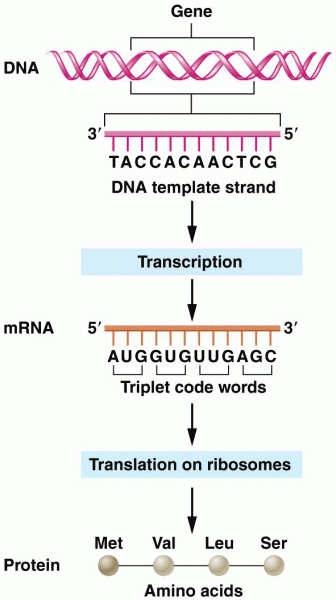
Answer to Question 1
Answer: 2, 3
Explanation: 2. The higher the educational level, the higher the societal productivity, which leads to better health outcomes through informed health choices. Health affects the national economic welfare, so an employed and healthy workforce is necessary for an economically healthy society. Chronic illness in a stable workforce impacts productivity, as people with chronic diseases may take more time off for the chronic illness. Lost productivity from illness has a direct effect on societal outcomes. Health insurance does not guarantee a healthy workforce as the insurance may be limiting in coverage or expensive to purchase.
3. The higher the educational level, the higher the societal productivity, which leads to better health outcomes through informed health choices. Health affects the national economic welfare, so an employed and healthy workforce is necessary for an economically healthy society. Chronic illness in a stable workforce impacts productivity, as people with chronic diseases may take more time off for the chronic illness. Lost productivity from illness has a direct effect on societal outcomes. Health insurance does not guarantee a healthy workforce as the insurance may be limiting in coverage or expensive to purchase.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: 1, 2, 3, 5
Explanation: 1. Culturally congruent care incorporates several components. These include cultural diversity, cultural awareness, cultural sensitivity, and cultural competence. Cultural diversity reflects the cultural differences that exist between health care professionals and a given population or cultural group. Cultural sensitivity involves assuming a learner role with respect to the culture of the population served. Cultural awareness encompasses providers' recognition of the influence of culture on health and health-related behaviors. Cultural competence is actions taken by providers in response to awareness and knowledge, or the performance of culturally congruent behaviors by providers or health care systems. Cultural imposition is an expectation that others will conform to the dictates of one's own culture.
2. Culturally congruent care incorporates several components. These include cultural diversity, cultural awareness, cultural sensitivity, and cultural competence. Cultural diversity reflects the cultural differences that exist between health care professionals and a given population or cultural group. Cultural sensitivity involves assuming a learner role with respect to the culture of the population served. Cultural awareness encompasses providers' recognition of the influence of culture on health and health-related behaviors. Cultural competence is actions taken by providers in response to awareness and knowledge, or the performance of culturally congruent behaviors by providers or health care systems. Cultural imposition is an expectation that others will conform to the dictates of one's own culture.
3. Culturally congruent care incorporates several components. These include cultural diversity, cultural awareness, cultural sensitivity, and cultural competence. Cultural diversity reflects the cultural differences that exist between health care professionals and a given population or cultural group. Cultural sensitivity involves assuming a learner role with respect to the culture of the population served. Cultural awareness encompasses providers' recognition of the influence of culture on health and health-related behaviors. Cultural competence is actions taken by providers in response to awareness and knowledge, or the performance of culturally congruent behaviors by providers or health care systems. Cultural imposition is an expectation that others will conform to the dictates of one's own culture.
5. Culturally congruent care incorporates several components. These include cultural diversity, cultural awareness, cultural sensitivity, and cultural competence. Cultural diversity reflects the cultural differences that exist between health care professionals and a given population or cultural group. Cultural sensitivity involves assuming a learner role with respect to the culture of the population served. Cultural awareness encompasses providers' recognition of the influence of culture on health and health-related behaviors. Cultural competence is actions taken by providers in response to awareness and knowledge, or the performance of culturally congruent behaviors by providers or health care systems. Cultural imposition is an expectation that others will conform to the dictates of one's own culture.