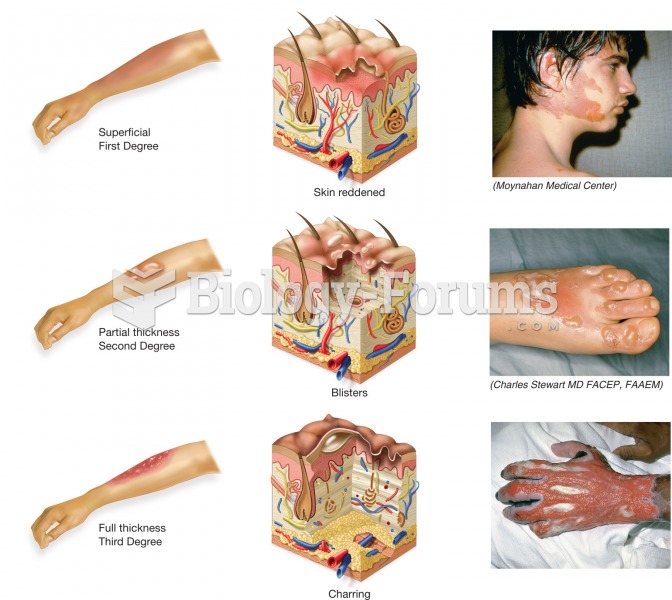
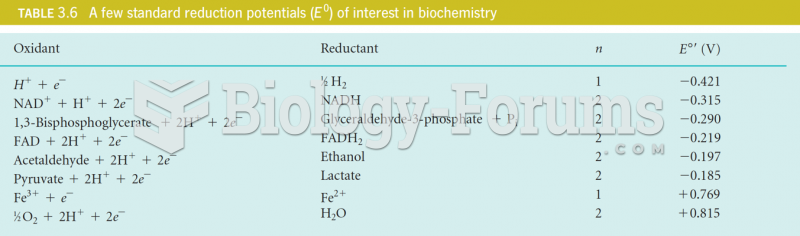
|
|
|
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
Elderly adults are at greatest risk of stroke and myocardial infarction and have the most to gain from prophylaxis. Patients ages 60 to 80 years with blood pressures above 160/90 mm Hg should benefit from antihypertensive treatment.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
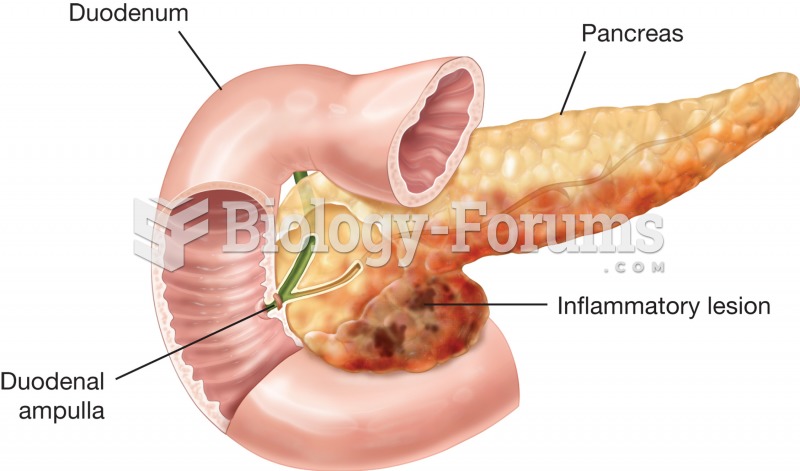 Pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas may be the result of a bacterial infection, trauma, or ch
Pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas may be the result of a bacterial infection, trauma, or ch
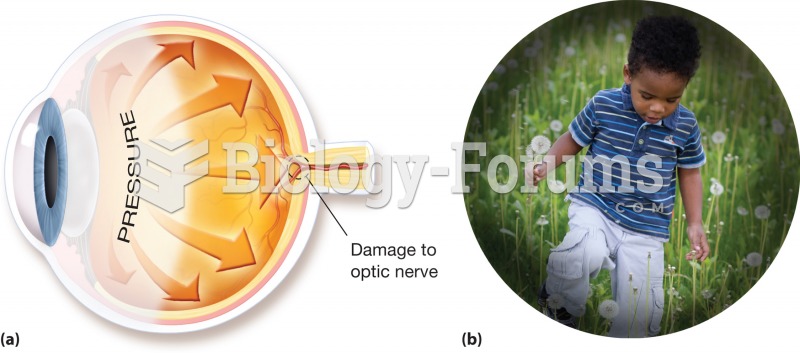 Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t
Glaucoma. (a) A buildup of pressure within the eye cavities, often caused by a blockage of vessels t