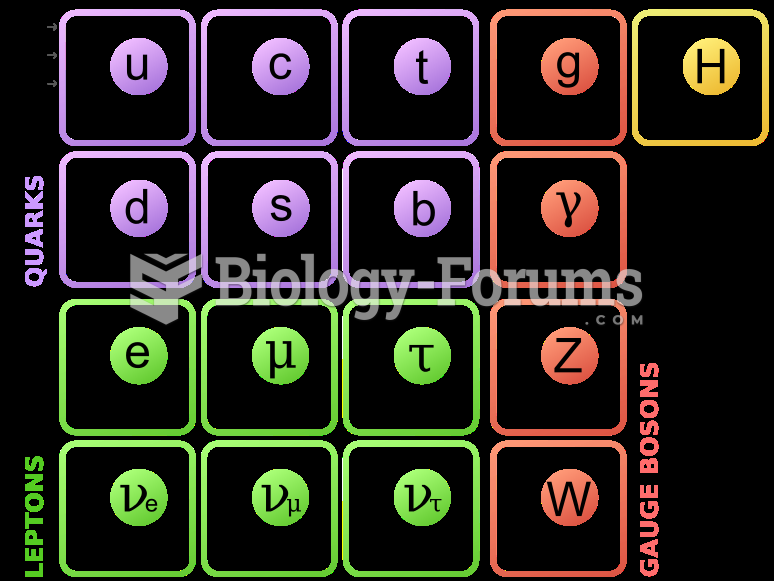
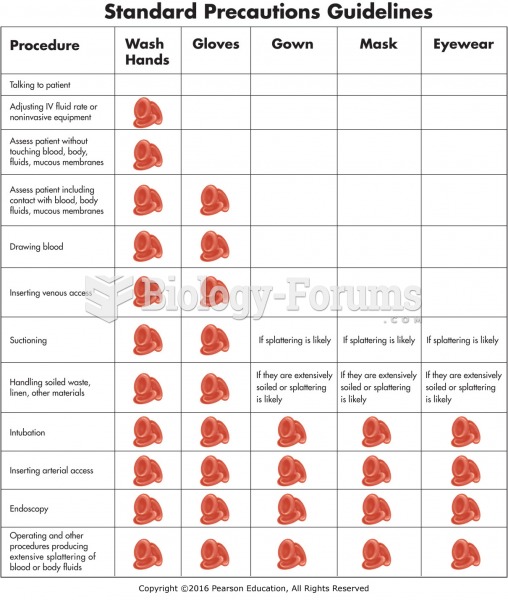
Answer to Question 1
Answer: An ideal response will:
1. Define the strict scrutiny standard, which requires that the discrimination must be the least restrictive way to achieve a permissible government goal.
2. Define the rational basis test, which refers to the fact that the government must have a rational foundation for the discrimination.
3. Identify racial classifications as those that are given strict scrutiny by the Supreme Court.
4. Identify a range of classifications such as age, wealth, mental capacity, and sexual orientation as those that are subject to the rational basis test.
5. Identify gender classifications as those that would be evaluated by the courts using an intermediate standard.
6. Provide an example of a law that would receive strict scrutiny, such as affirmative action programs based on race.
7. Provide an example of a law that would be judged under the rational basis test, such as a law requiring those over the age of 80 to get a new driver's license more frequently than those 80 years old or younger.
8. Provide an example of a law that would be evaluated using an intermediate standard, such as a law permitting women to marry at age 14, but not permitting men to marry until age 17.
9. Indicate agreement or disagreement with this three-tiered approach. Answers will vary, but some may argue that all forms of discrimination are equally troubling and should all be treated the same. Others may argue that some sorts of discrimination may be reasonable under some circumstances, but other sorts of discrimination are seldom tolerable (giving examples).
Answer to Question 2
Answer: An ideal response will:
1. Describe the Equal Rights Amendment as a proposal that would have enshrined gender equality in the Constitution.
2. Explain the concerns of the ERA's opponents, such as the fear that it could disrupt the traditional family relationship and put women on the front lines in the armed forces.
3. Compare the ERA and the Nineteenth Amendment, noting that both expand civil rights for women.
4. Contrast the ERA with the Nineteenth Amendment, noting that the Nineteenth Amendment addresses only the right to vote, while the ERA addresses a much broader array of civil rights.
5. Evaluate how the ERA has impacted civil rights in the United States. The most common assessment will be that the ERA has had little effect on civil rights in the United States because it never became law. Others, however, could argue that the ERA has impacted civil rights by keeping women's rights on the front burner, despite the fact that it never became law.