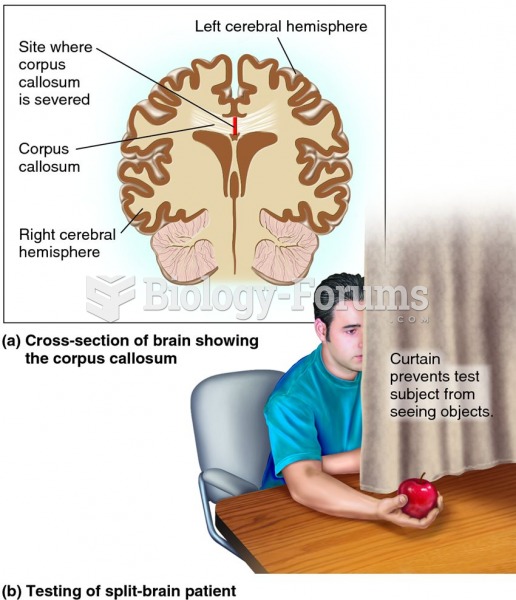
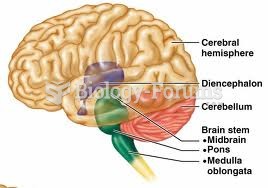
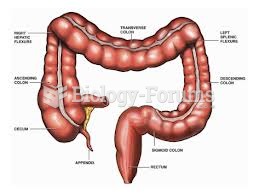
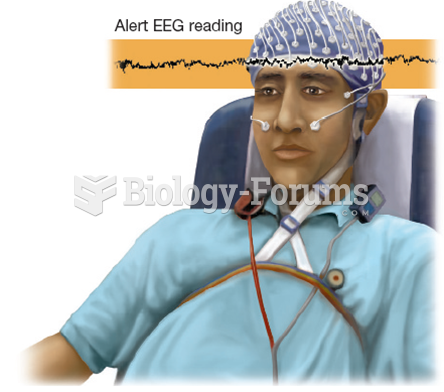
|
|
|
Did you know?
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Did you know?
Certain rare plants containing cyanide include apricot pits and a type of potato called cassava. Fortunately, only chronic or massive ingestion of any of these plants can lead to serious poisoning.
Did you know?
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Did you know?
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Did you know?
The human body produces and destroys 15 million blood cells every second.