|
|
|
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
Vaccines prevent between 2.5 and 4 million deaths every year.
In 1835 it was discovered that a disease of silkworms known as muscardine could be transferred from one silkworm to another, and was caused by a fungus.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
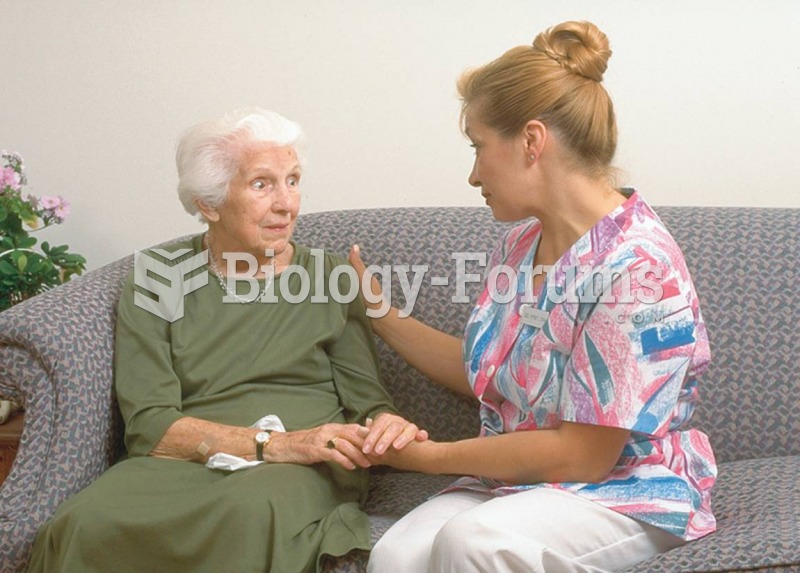
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.