Answer to Question 1
ANSWER: Because the Sun radiates almost half of its energy as visible light, all visible wavelengths from the midday Sun reach the cones, and the Sun usually appears nearly white. A star that is cooler than our Sun radiates most of its energy at slightly longer wavelengths; therefore, it appears redder. On the other hand, a star much hotter than our Sun radiates more energy at shorter wavelengths and thus appears bluer. A star whose temperature is about the same as the Suns appears white.
Answer to Question 2
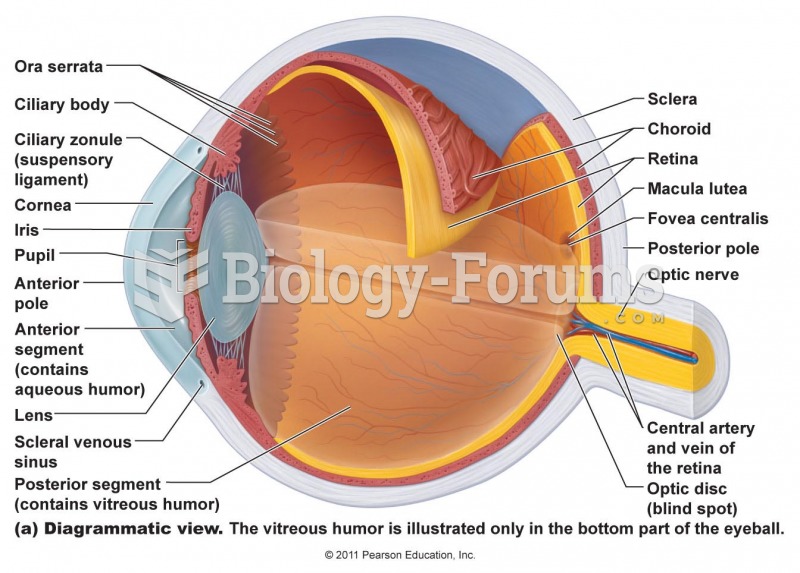
ANSWER: We perceive light because radiant energy from the Sun travels outward in the form of electromagnetic waves. When these waves reach the human eye, they stimulate antenna-like nerve endings in the retina. These antennae are of two typesrods and cones. The rods respond to all wavelengths of visible light and give us the ability to distinguish light from dark. If people possessed rod-type receptors only, then only black and white vision would be possible. The cones respond to specific wavelengths of visible light. Radiation with a wavelength between 0.4 and 0.7 micrometers (m) strikes the cones, which immediately fire an impulse through the nervous system to the brain, and we perceive this impulse as the sensation of color. (Color blindness is caused by missing or malfunctioning cones.) Wavelengths of radiation shorter than 0.4 m, or longer than 0.7 m, do not stimulate color vision in humans.