Answer to Question 1
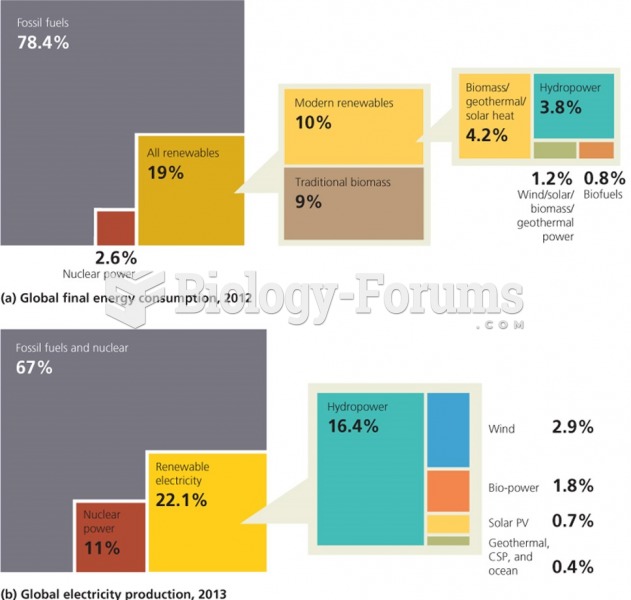
Answer: The rising costs of fossil fuels and concerns about global warming are stimulating interest in alternative sources of energy, especially those that produce electricity. Nuclear power supplies about one-third of all electricity in Europe, and about 20 percent in the U.S. Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan also rely on nuclear-generated electricity. Despite the fact that nuclear power is relatively clean when power plants are functioning correctly, it presents serious problems of potential accidents and the generation of radioactive waste.
Potential for accidents: Three major incidents have had dramatic influences on the nuclear power industry. In March 1979, a power plant at Three Mile Island experienced a loss of coolant that contributed to a partial meltdown of the reactor core. The incident was relatively minor in terms of radioactive releases and no one was injured, but it caused a dramatic increase in public awareness of the hazards involved. The second one is considered the greatest nuclear catastrophe to date. It occurred in 1986, in a nuclear power plant at Chernobyl, Ukraine, near the border with Belarus. The accident has caused over 3,500 deaths, and potentially many more from subsequent cancers. The impact of this accident extended through Europe, causing bans on the sale of milk and fresh vegetables because of possible contamination by radioactive fallout. The third is the catastrophe at the Fukushima plant in Japan in March 2011, which has once again raised fears surrounding nuclear power. It came at a time when, in many areas including the United States, interest in building new nuclear power plants was starting to grow. It remains to be seen whether public faith in nuclear power will recover sufficiently to justify building new plants, and whether enough guarantees can be put in place to justify such restored faith.
Nuclear waste disposal: At the present time, there is no effective way for disposing of nuclear waste besides storing them on, or off-site. Some countries reprocess spent nuclear rods, but we still have not come up with a definitive way of dealing with the eventual waste that is generated.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Renewable energy includes a diverse range of technologies, from traditional wood-burning, to hydroelectricity that has been used for more than a century, to technologies such as solar and wind-generated electricity, ethanol and biodiesel, photovoltaics, tidal energy, and geothermal power production that are emerging today or are still in development.
Wood fuel is a substantial source of energy for cooking and heating, mainly in poor countries. Hydroelectricity is the most important renewable source for commercial power, producing about 6 percent of global commercial energy. All the other renewable technologies together are responsible for less than 2 percent of global energy production. Many forms of plant matter can be converted to biofuels, liquid or gaseous fuels that can be burned, for example, in modern automobiles. But, it takes a significant amount of land to produce the feedstock for biofuels, taking much land that could have been used for food. Also, the amount of fuel energy that is produced from manufacturing ethanol from corn or biodiesel from soybeans is small after one accounts for the amount of fuel consumed for tractor fuel, fertilizer, and other energy inputs to biofuel production.
Canada, China, Brazil, and the United States are the largest producers of hydroelectric power in the world. Most of the best sites for hydroelectric generation are already in use in the United States and Europe, but in many areas, there is considerable undeveloped potential. Opposition to construction of big dams and reservoirs is strong among people who fear the environmental damage they cause, such as loss of farmland or animal habitat.
At present, solar energy is used in two principal ways: thermal energy and photovoltaic electricity production. Solar thermal energy is heat collected directly from sunshine in collectors on the roofs of buildings. The heat absorbed by these collectors is then carried in water or other liquids to the places where it is needed. Photovoltaic electric production is a direct conversion of solar energy to electricity in photovoltaic cells. Photovoltaic power is competitive in price with conventional electricity in much of the world, and offers considerable potential as economies of scale bring prices down. However, it suffers from the problem that solar energy is not reliable: it varies with season and with weather.
Geothermal energy use in the United States is mainly in the form of electricity production at a handful of sites, led by California's Geysers plant. (In addition, several new uses for geothermal energy are being utilized, including shafts drilled deep into the subsoil beneath new construction in urban areas.) Wind generation of electricity is one of the fastest-growing renewable energy technologies today, although it still amounts to less than 2 percent of total U.S. electricity production. Environmentalists are divided on wind energy: some favor wind generation because it is renewable and pollution-free, while others oppose itwhere it involves especially large windmills and turbineson the grounds of visual impacts and its hazards to birds.
Answer to Question 3
Answer: FALSE