Answer to Question 1
Answer: Government subsidies are financial and monetary incentives provided by the government to some or all farmers in order to affect the supply and price of certain commodities. The U.S. government has three policies that are supposed to address the problem of excess productive capacity:
First, farmers are encouraged to avoid producing crops in excess supply. Because soil erosion is a constant threat, farmers are encouraged to plant fallow crops, such as clover, to restore nutrients to the soil and to help hold the soil in place. These crops can be used for hay, forage for pigs, or to produce seeds for sale.
Second, the government pays farmers when certain commodity prices are low. The government sets a target price for the commodity and pays farmers the difference between the price they receive in the market and a target price set by the government as a fair level for the commodity. The target prices are calculated to give farmers the same price for the commodity today as in the past, when compared to other consumer goods and services.
Finally, the government buys surplus production and sells or donates it to foreign governments. In addition, low-income Americans receive food stamps in part to stimulate their purchase of additional food.
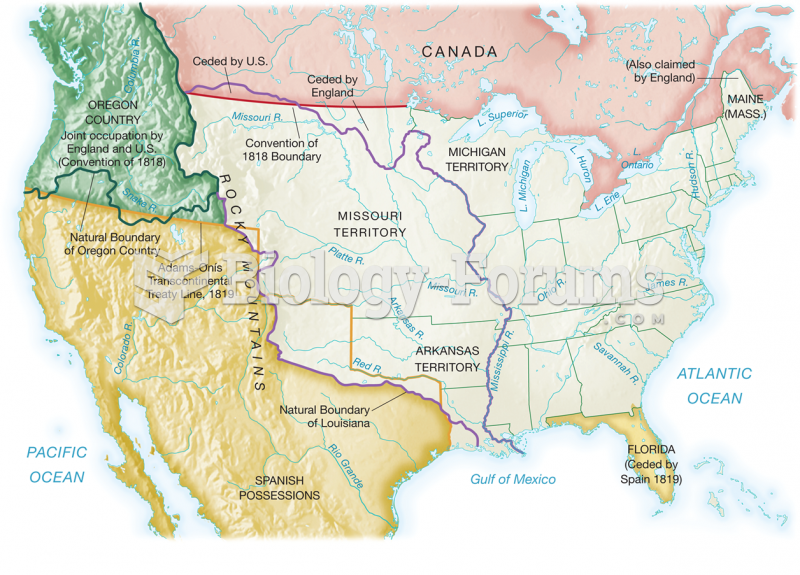
Government policies in developed countries point out a fundamental irony in worldwide agricultural patterns. In developed countries, farmers are encouraged to grow less food, whereas some developing countries struggle to increase food production to match the rate of growth in the population.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: Commercial agriculture is generally practiced in developed countries and is undertaken primarily to generate products for sale off the farm to food-processing companies. Subsistence agriculture, on the other hand, generally practiced in developing countries, is designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family.
Subsistence and commercial farming differ in several key ways, including farm size, use of machinery and percentage of farmers in the society.
Farm Size: The average farm size is much larger in commercial agriculture, in part as a result of mechanization. In the U.S., for example, farms average about 161 hectares (418 acres), compared to about 1 hectare in China. Commercial agriculture is dominated by a handful of large farms. In the United States, the largest 5 percent of farms produced 75 percent of the country's total agriculture. Despite their size, most commercial farms in developed countries are family owned and operated.
The percentage of farmers in society: In developed countries around 5 percent of workers are engaged directly in farming, compared to around 50 percent in developing countries . The percentage of farmers is even lower in North America, where only about 2 percent are engaged directly in farming. Yet the small percentage of farmers in the United States and Canada produces enough food not only for themselves and the rest of the region but also a surplus to feed people elsewhere. The number of farmers declined dramatically in developed countries during the twentieth century.
Use of machinery: In developed countries, a small number of farmers can feed many people because they rely on machinery to perform work, rather than relying on people or animals. In developing countries, farmers do the work with hand tools and animal power. Traditionally, the farmer or local crafts people made equipment from wood, but beginning in the late eighteenth century, factories produced farm machinery.
Answer to Question 3
Answer: Subsistence agriculture is agriculture designed primarily to provide food for direct consumption by the farmer and the farmer's family. It is generally practiced in developing countries. It is generally characterized by small farms, a high percentage of farmers, and because the people are typically poor, very few machines. There are three types of subsistence agriculture practiced in developing countries. These are shifting cultivation, intensive subsistence and pastoral nomadism.
Shifting cultivation, sometimes called slash and burn, is practiced in much of the world's Humid Low-Latitude regions, which have relatively high temperatures and abundant rainfall. Each year, in an area surrounding the village that is designated for planting, villagers remove the dense vegetation using axes and machetes. The debris is burned before planting is done. The fresh ashes provide the soil with much needed nutrients. The newly cleared area, called a swidden, can support crops only briefly, usually 3 years or less, before soil nutrients are depleted. After the soil is depleted, villagers identify a new plot for cultivation, leaving the previous one to fallow for many years.
Intensive subsistence is practiced primarily in densely populated East, South, and Southeast Asia. Because the agricultural density is so high in these regions, families must produce enough food for their survival from a very small area of land. Most of the work is done by hand or with animals rather than with machines, in part due to abundant labor, but largely from lack of funds to buy equipment.
In dry climates, where planting crops is impossible, pastoral nomadism has evolved as the predominant form of subsistence agriculture. It is based on the herding of domesticated animals. Pastoral nomads live primarily in the large belt of arid and semiarid land that includes North Africa, the Middle East, and parts of Central Asia. The Bedouins of Saudi Arabia and North Africa and the Masai of East Africa are examples of nomadic groups. Pastoral nomads depend primarily on animals rather than crops for survival. The animals provide milk, and their skins and hair are used for clothing and tents.