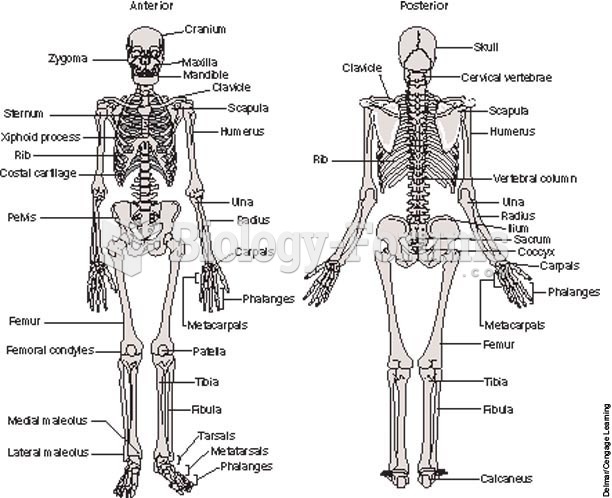
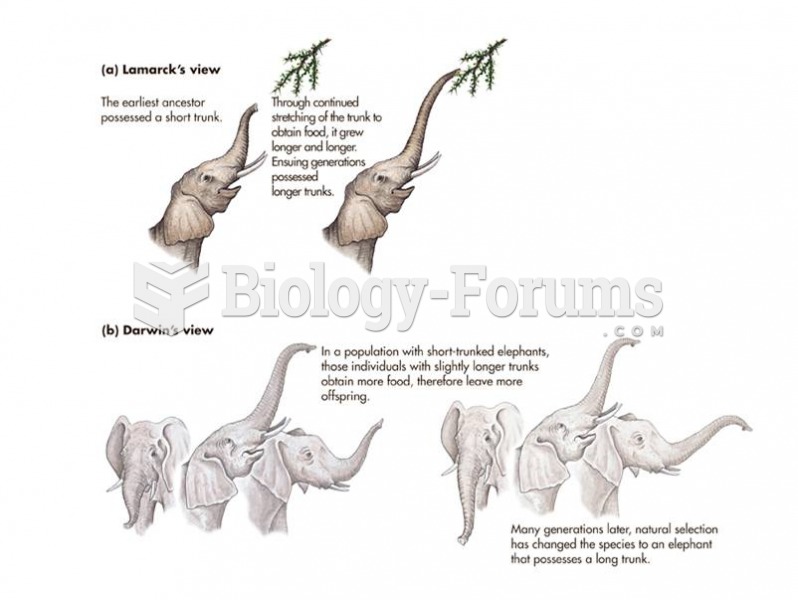
Answer to Question 1
- How does the description of real talk in Women's Ways of Knowing reflect the stage of cognitive development that Perry called Constructed Knowledge? Compare and contrast real talk to didactic talk.
- Constructed knowledge is characterized by a recognition of the interrelatedness of knowledge, knowing and the knower. Based on intense self-reflection, women in this stage view knowledge as a constant process of construction, deconstruction and reconstruction, often in concert with others.
- Constructivists make a distinction between really talking and what they consider to be didactic talk:
- In didactic talk, each participant may report experience, but there is no attempt among participants to join together to arrive at some new understanding.
- Real talk requires careful listening; it implies a mutually shared agreement that together you are creating the optimum setting so that half-baked or emergent ideas can grow. Real talk reaches deep into the experience of each participant; it also draws on the analytical abilities of each.
Answer to Question 2
- Phenomenal reality: Kant's term for the world as we experience (constitute) it. Known through the senses.
- Noumenal reality: Kant's term for the world that exists beyond our perceptions, reality in-itself. Known only through the application of pure reason, which in addition to confirming the existence of objective reality also gives us knowledge of the possibility of genuine personal freedom and the existence of a universal moral law (the categorical imperative).
- Kant identified three other transcendental ideas that we use to synthesize (or bridge the gap) between the phenomenal and noumenal realities: self, cosmos, and God. These are universal a priori ideas that regulate and make possible the phenomenal world, but because they refer to possibilities that exist in the noumenal world they can never be empirically verified.