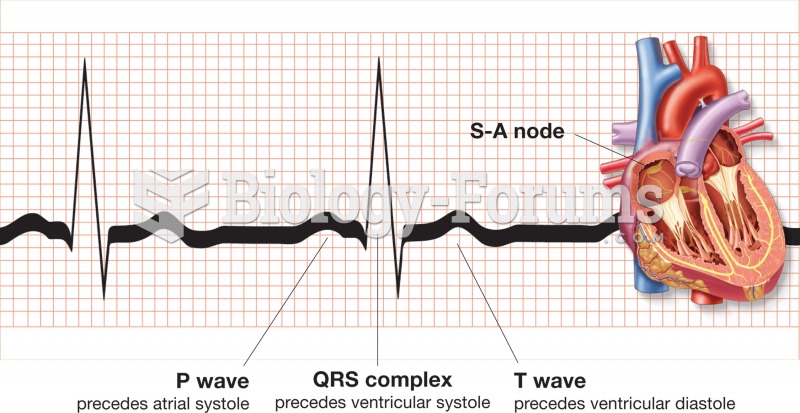
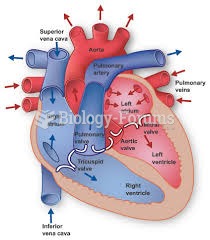
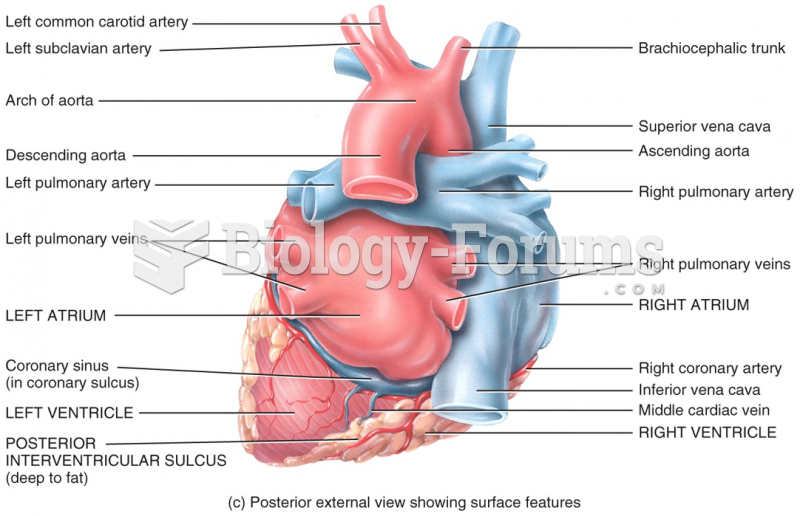
|
|
|
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
Approximately one in three babies in the United States is now delivered by cesarean section. The number of cesarean sections in the United States has risen 46% since 1996.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
Signs and symptoms that may signify an eye tumor include general blurred vision, bulging eye(s), double vision, a sensation of a foreign body in the eye(s), iris defects, limited ability to move the eyelid(s), limited ability to move the eye(s), pain or discomfort in or around the eyes or eyelids, red or pink eyes, white or cloud spots on the eye(s), colored spots on the eyelid(s), swelling around the eyes, swollen eyelid(s), and general vision loss.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.