|
|
|
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
About 600,000 particles of skin are shed every hour by each human. If you live to age 70 years, you have shed 105 pounds of dead skin.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.
According to the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology, more than 50 million Americans have some kind of food allergy. Food allergies affect between 4 and 6% of children, and 4% of adults, according to the CDC. The most common food allergies include shellfish, peanuts, walnuts, fish, eggs, milk, and soy.
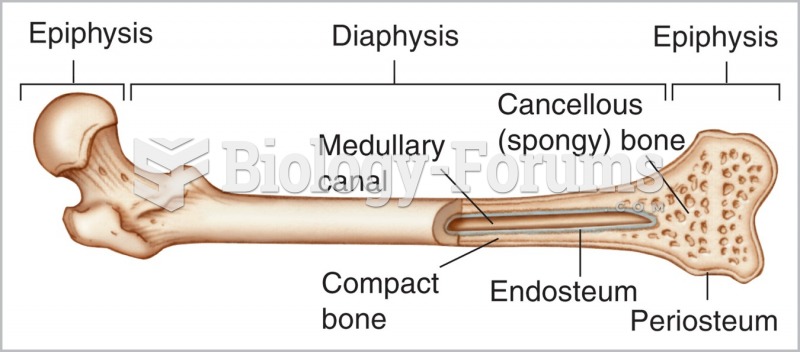
Adolescents often feel clumsy during puberty because during this time of development, their hands and feet grow faster than their arms and legs do. The body is therefore out of proportion. One out of five adolescents actually experiences growing pains during this period.