Answer to Question 1
ANS: B
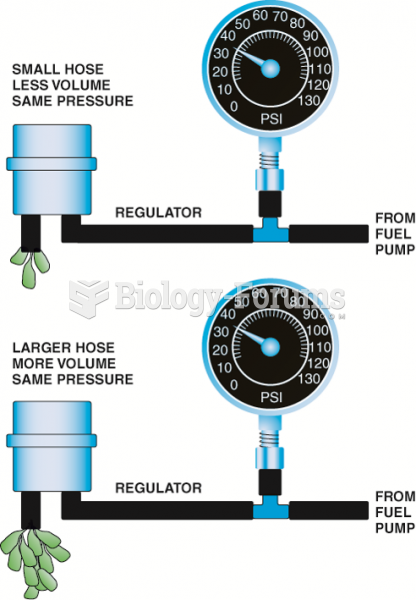
With the increased popularity of noninvasive positive pressure ventilation and continued exten-sive use of invasive ventilation, negative pressure ventilators are rarely used today for ventilatory support in postacute care settings. The original negative pressure ventilator was the iron lung, popularized by postpolio patients needing ventilator assistance. For practical reasons, the cum-bersome iron lung was essentially replaced by the chest cuirass and wrap or pneumosuit. The chest cuirass (a rigid shell) and wrap-type systems (nylon fabric surrounding a semicylindrical tentlike support) are simply enclosures that allow application of negative pressure to the thorax. Thus, these devices require a separate electrically powered negative pressure generator. An exam-ple of a negative pressure generator used to power cuirass or wrap-type systems is the Respironics NEV-100.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: C
With the increased popularity of noninvasive positive pressure ventilators and continued exten-sive use of invasive ventilation, negative pressure ventilators are rarely used today for ventilatory support in postacute care settings. The original negative pressure ventilator was the iron lung, popularized by postpolio patients needing ventilator assistance. For practical reasons, the cum-bersome iron lung was essentially replaced by the chest cuirass and wrap or pneumosuit. The chest cuirass (a rigid shell) and wrap-type systems (nylon fabric surrounding a semicylindrical tentlike support) are simply enclosures that allow application of negative pressure to the thorax. Thus, these devices require a separate electrically powered negative pressure generator. An exam-ple of a negative pressure generator used to power cuirass or wrap-type systems is the Respironics NEV-100.