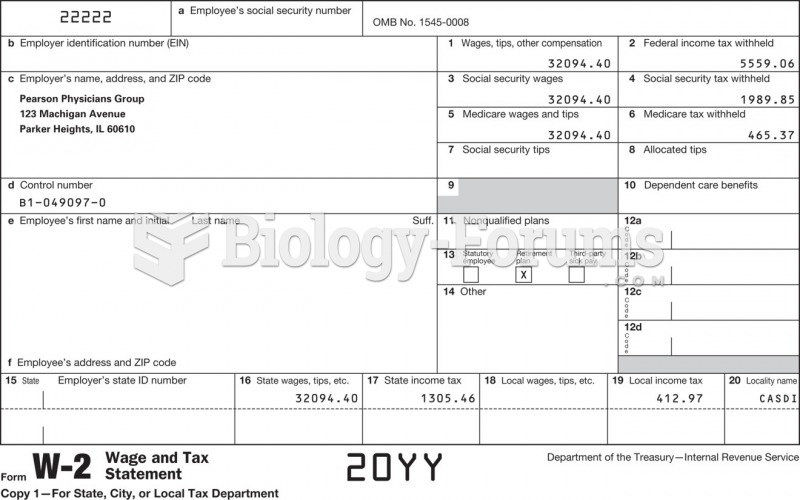
|
|
|
About 3.2 billion people, nearly half the world population, are at risk for malaria. In 2015, there are about 214 million malaria cases and an estimated 438,000 malaria deaths.
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Although the Roman numeral for the number 4 has always been taught to have been "IV," according to historians, the ancient Romans probably used "IIII" most of the time. This is partially backed up by the fact that early grandfather clocks displayed IIII for the number 4 instead of IV. Early clockmakers apparently thought that the IIII balanced out the VIII (used for the number 8) on the clock face and that it just looked better.
Carbamazepine can interfere with the results of home pregnancy tests. If you are taking carbamazepine, do not try to test for pregnancy at home.
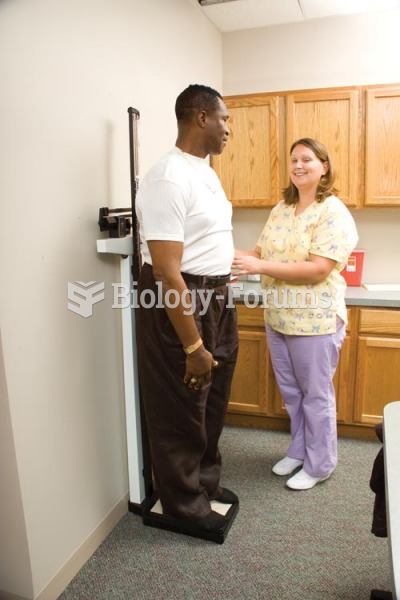
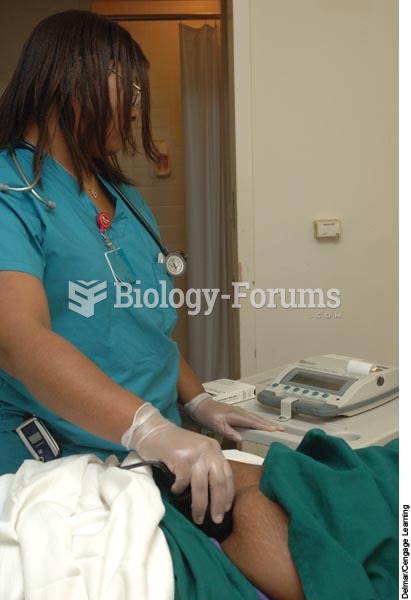
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.