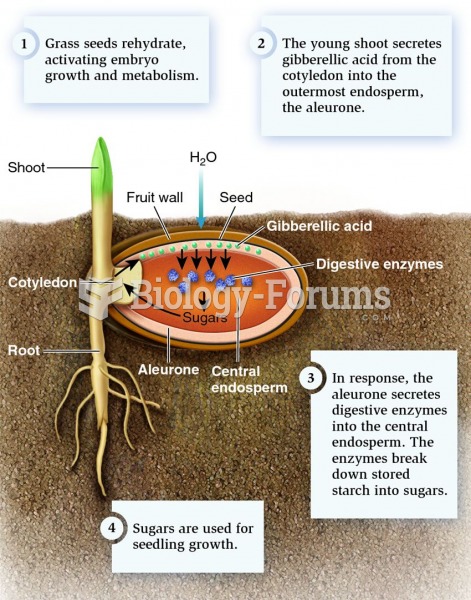
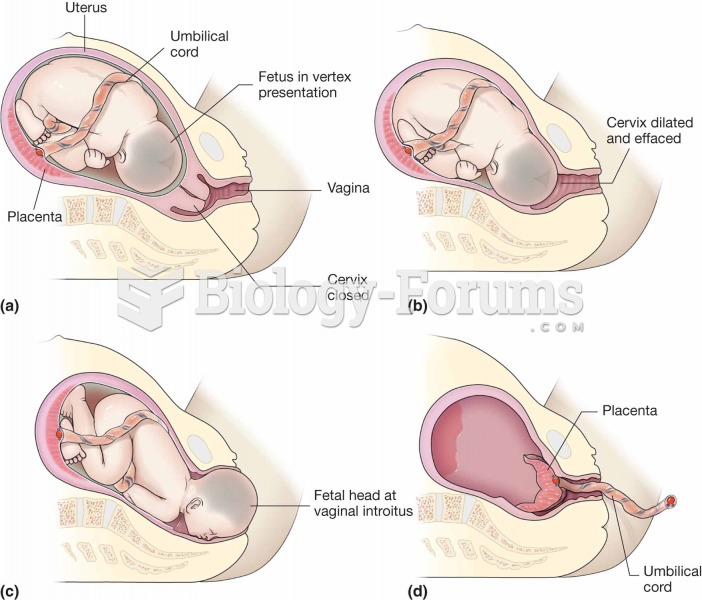
|
|
|
Asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the world. Most children who develop asthma have symptoms before they are 5 years old.
Though the United States has largely rejected the metric system, it is used for currency, as in 100 pennies = 1 dollar. Previously, the British currency system was used, with measurements such as 12 pence to the shilling, and 20 shillings to the pound.
The top five reasons that children stay home from school are as follows: colds, stomach flu (gastroenteritis), ear infection (otitis media), pink eye (conjunctivitis), and sore throat.
Many medications that are used to treat infertility are injected subcutaneously. This is easy to do using the anterior abdomen as the site of injection but avoiding the area directly around the belly button.
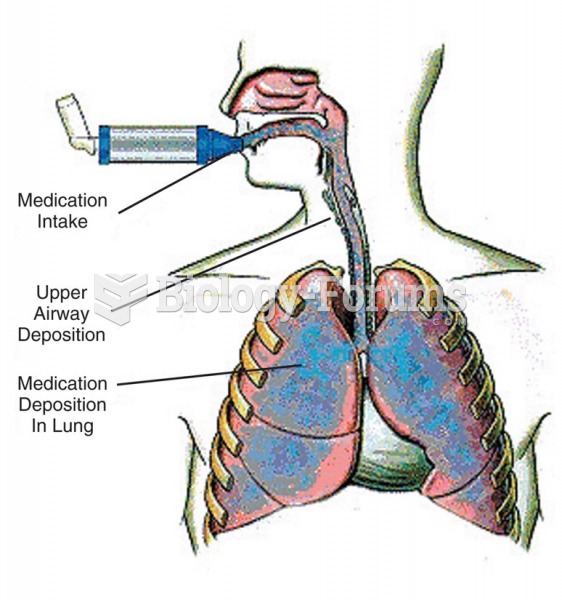
According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, lung disease is the third leading killer in the United States, responsible for one in seven deaths. It is the leading cause of death among infants under the age of one year.