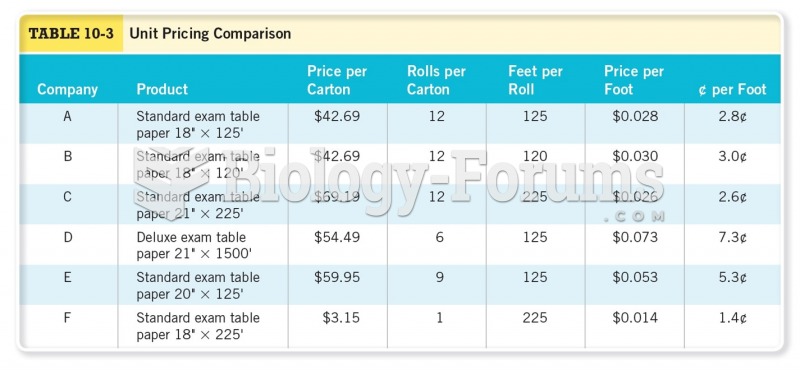
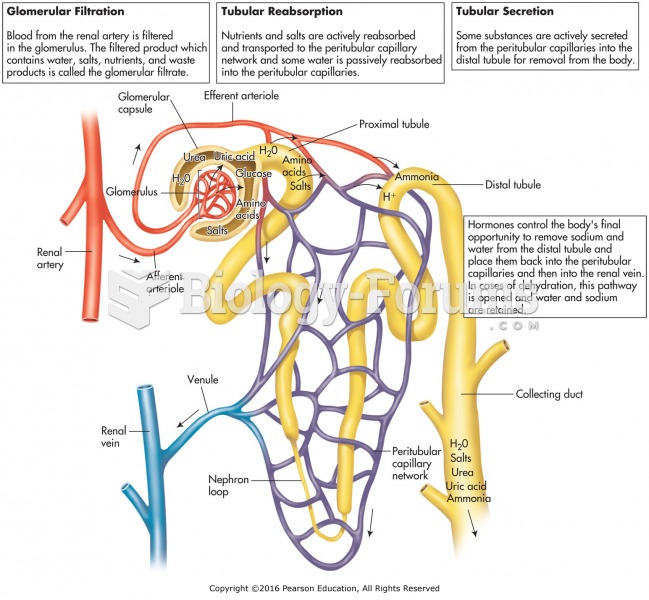
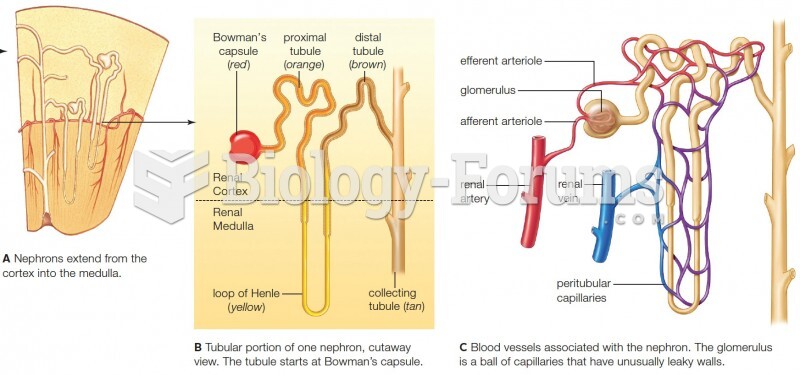
|
|
|
On average, the stomach produces 2 L of hydrochloric acid per day.
Human neurons are so small that they require a microscope in order to be seen. However, some neurons can be up to 3 feet long, such as those that extend from the spinal cord to the toes.
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Many medications that are used to treat infertility are injected subcutaneously. This is easy to do using the anterior abdomen as the site of injection but avoiding the area directly around the belly button.
Earwax has antimicrobial properties that reduce the viability of bacteria and fungus in the human ear.