|
|
|
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
Drug abusers experience the following scenario: The pleasure given by their drug (or drugs) of choice is so strong that it is difficult to eradicate even after years of staying away from the substances involved. Certain triggers may cause a drug abuser to relapse. Research shows that long-term drug abuse results in significant changes in brain function that persist long after an individual stops using drugs. It is most important to realize that the same is true of not just illegal substances but alcohol and tobacco as well.
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
 When the United States gets stuck over a controversial issue—usually something a divided Congress ca
When the United States gets stuck over a controversial issue—usually something a divided Congress ca
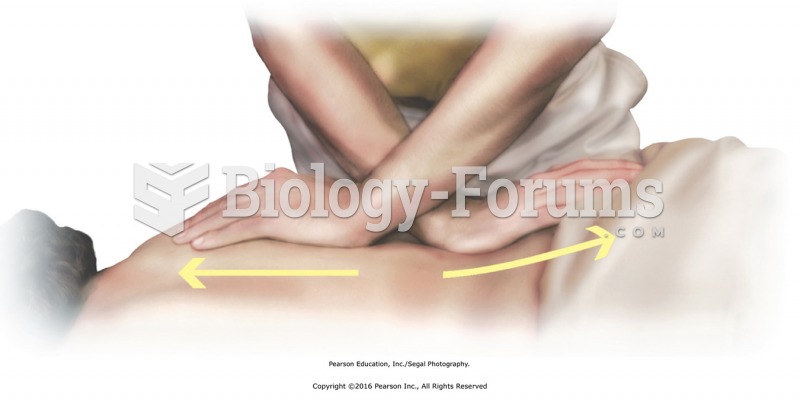 Stand facing the side of the table and apply cross-handed stretches for the subcutaneous fascia. ...
Stand facing the side of the table and apply cross-handed stretches for the subcutaneous fascia. ...