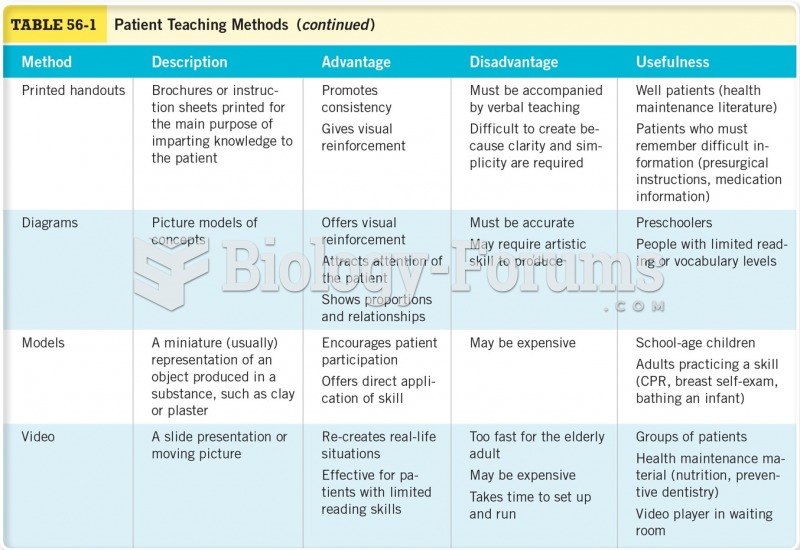
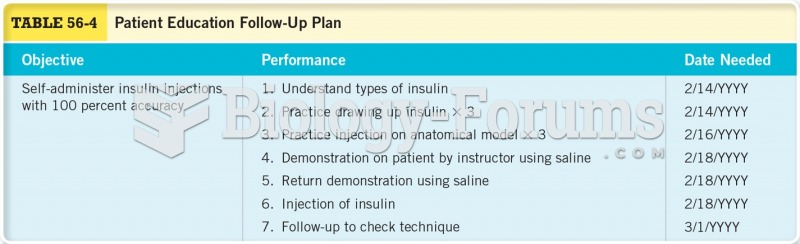
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
According to the Migraine Research Foundation, migraines are the third most prevalent illness in the world. Women are most affected (18%), followed by children of both sexes (10%), and men (6%).
Did you know?
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Did you know?
There are more bacteria in your mouth than there are people in the world.
Did you know?
Famous people who died from poisoning or drug overdose include, Adolf Hitler, Socrates, Juan Ponce de Leon, Marilyn Monroe, Judy Garland, and John Belushi.
Did you know?
The immune system needs 9.5 hours of sleep in total darkness to recharge completely.