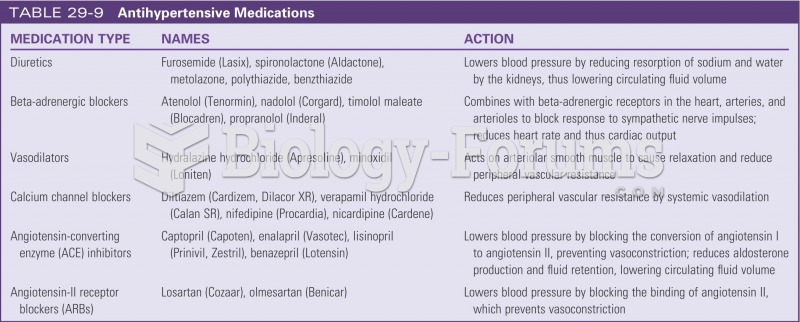
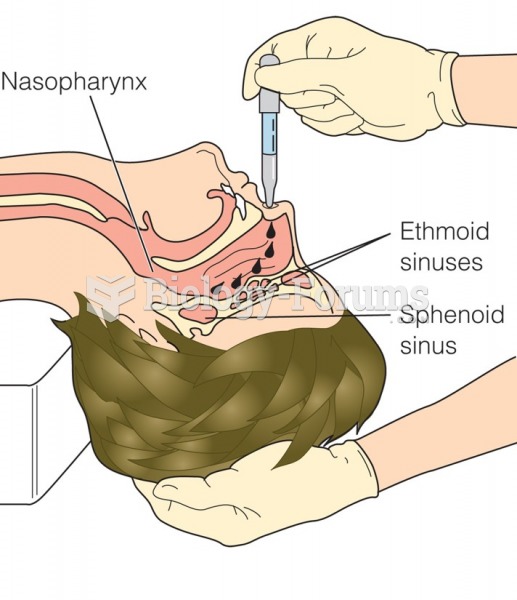
|
|
|
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Bisphosphonates were first developed in the nineteenth century. They were first investigated for use in disorders of bone metabolism in the 1960s. They are now used clinically for the treatment of osteoporosis, Paget's disease, bone metastasis, multiple myeloma, and other conditions that feature bone fragility.
A seasonal flu vaccine is the best way to reduce the chances you will get seasonal influenza and spread it to others.
Asthma occurs in one in 11 children and in one in 12 adults. African Americans and Latinos have a higher risk for developing asthma than other groups.
ACTH levels are normally highest in the early morning (between 6 and 8 A.M.) and lowest in the evening (between 6 and 11 P.M.). Therefore, a doctor who suspects abnormal levels looks for low ACTH in the morning and high ACTH in the evening.