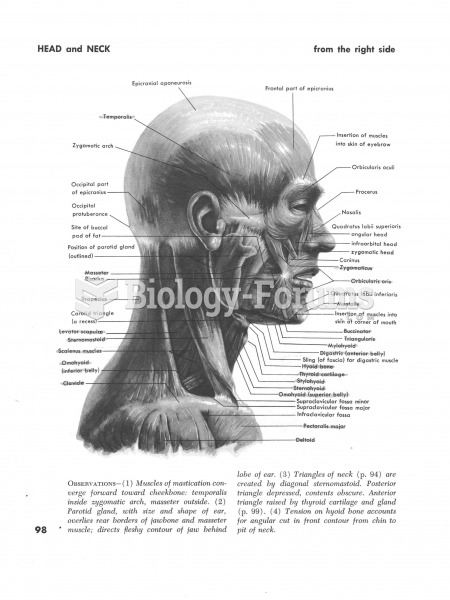
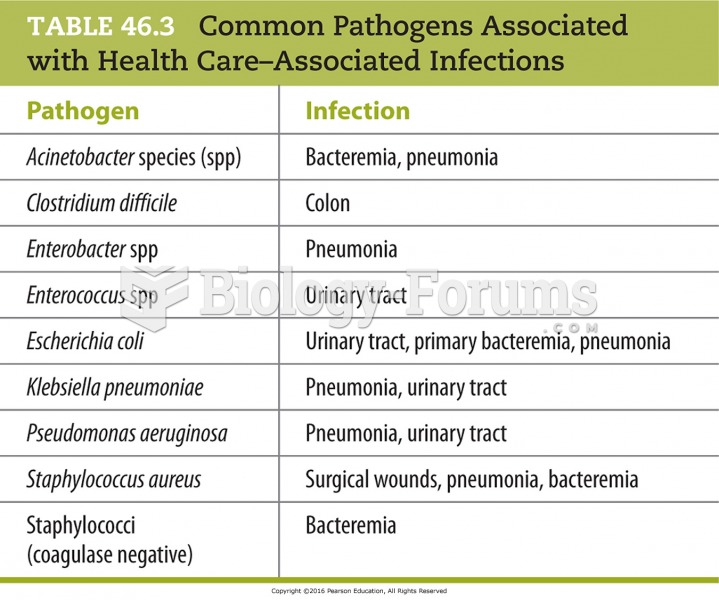
|
|
|
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
The senior population grows every year. Seniors older than 65 years of age now comprise more than 13% of the total population. However, women outlive men. In the 85-and-over age group, there are only 45 men to every 100 women.
Blood in the urine can be a sign of a kidney stone, glomerulonephritis, or other kidney problems.
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.