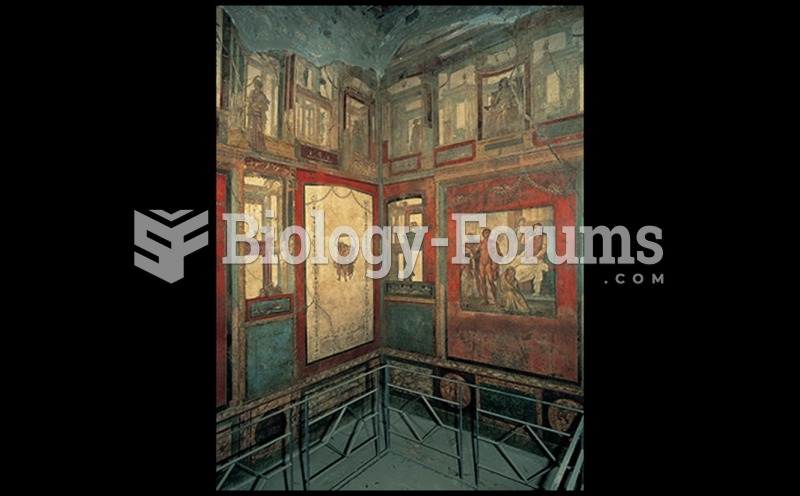
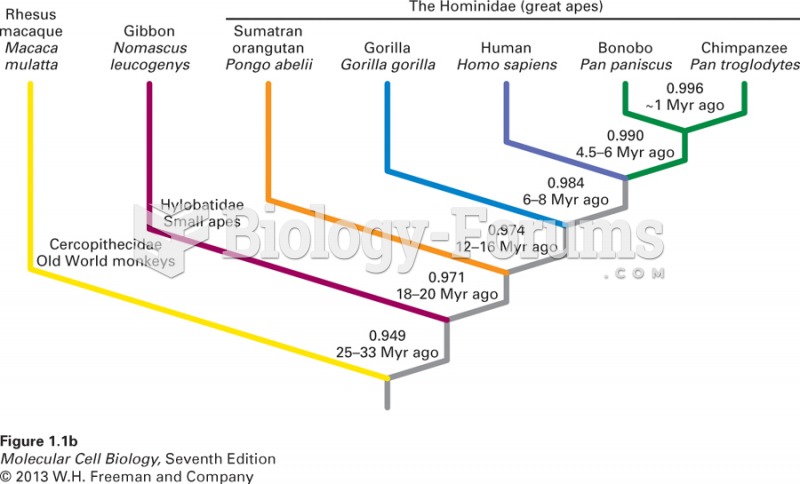
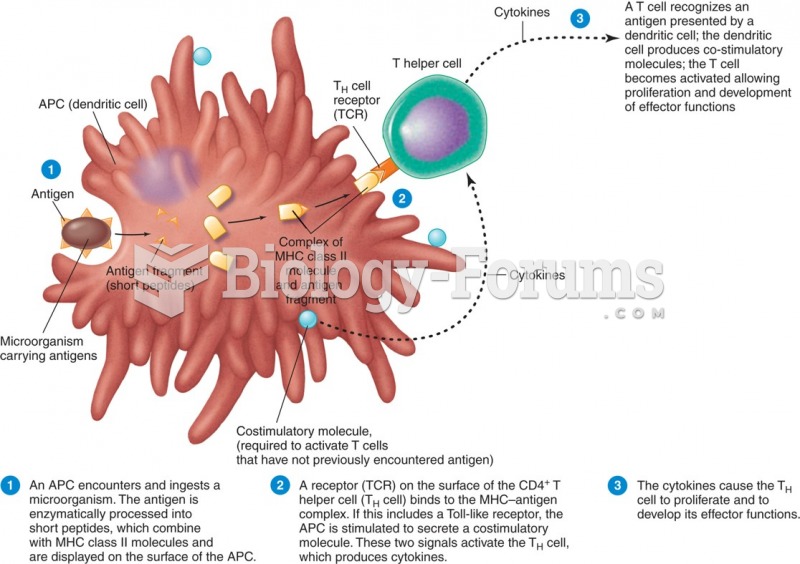
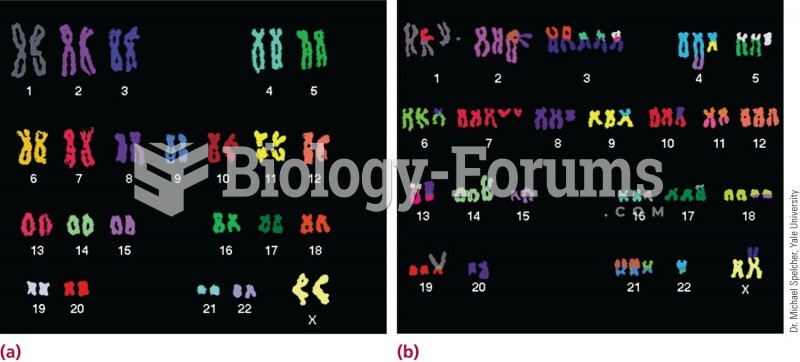
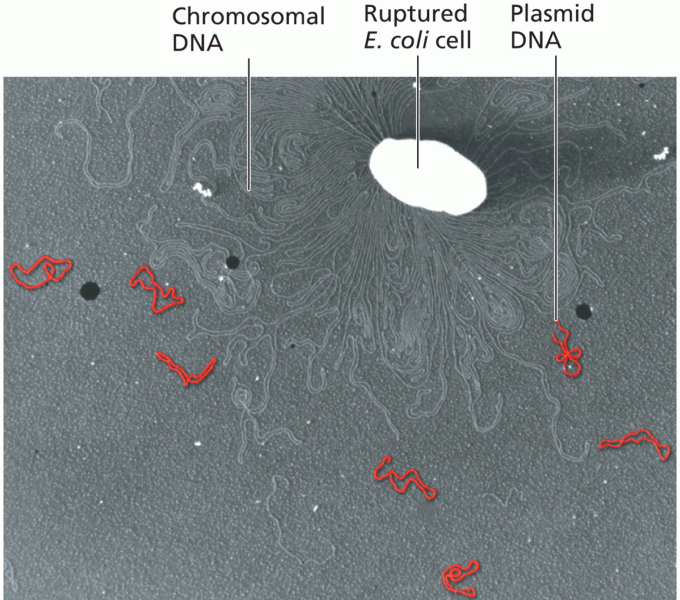
|
|
|
There are immediate benefits of chiropractic adjustments that are visible via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It shows that spinal manipulation therapy is effective in decreasing pain and increasing the gaps between the vertebrae, reducing pressure that leads to pain.
Malaria mortality rates are falling. Increased malaria prevention and control measures have greatly improved these rates. Since 2000, malaria mortality rates have fallen globally by 60% among all age groups, and by 65% among children under age 5.
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
A good example of polar molecules can be understood when trying to make a cake. If water and oil are required, they will not mix together. If you put them into a measuring cup, the oil will rise to the top while the water remains on the bottom.
Tobacco depletes the body of vitamins A, C, and E, which can result in any of the following: dry hair, dry skin, dry eyes, poor growth, night blindness, abscesses, insomnia, fatigue, reproductive system problems, sinusitis, pneumonia, frequent respiratory problems, skin disorders, weight loss, rickets, osteomalacia, nervousness, muscle spasms, leg cramps, extremity numbness, bone malformations, decayed teeth, difficulty in walking, irritability, restlessness, profuse sweating, increased uric acid (gout), joint damage, damaged red blood cells, destruction of nerves, infertility, miscarriage, and many types of cancer.