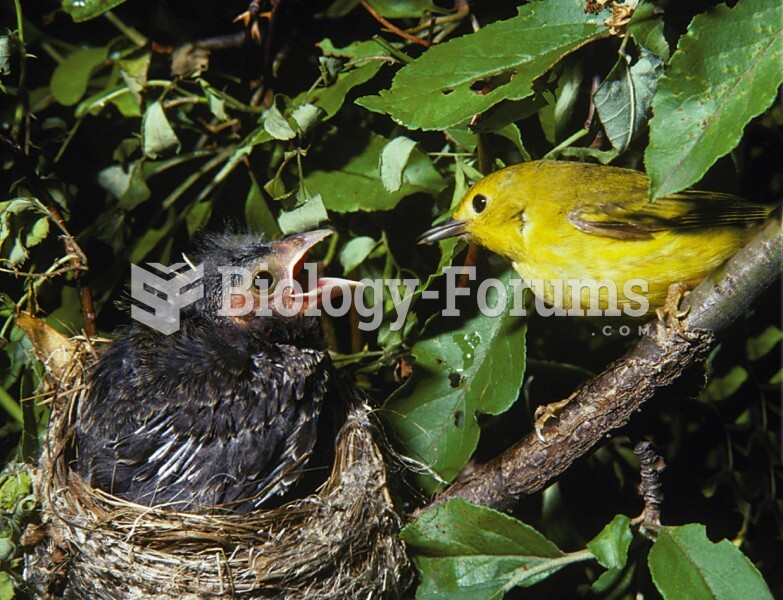
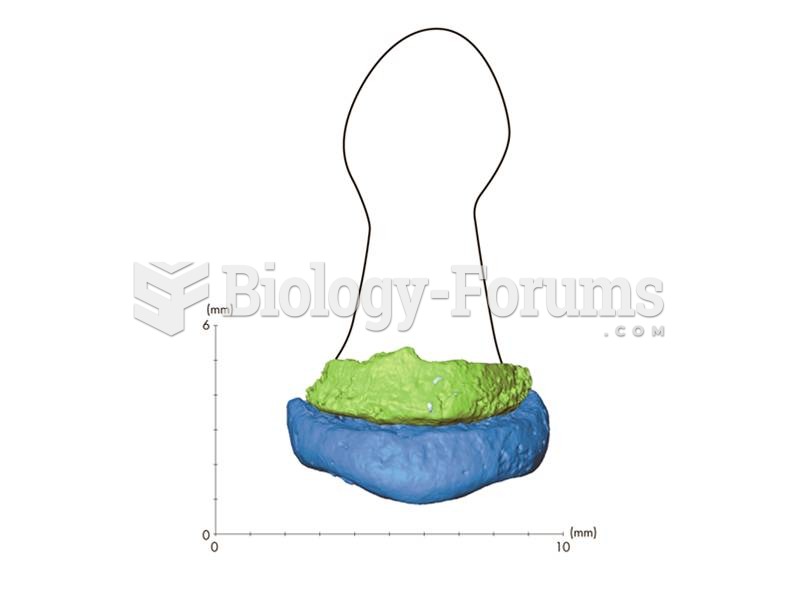
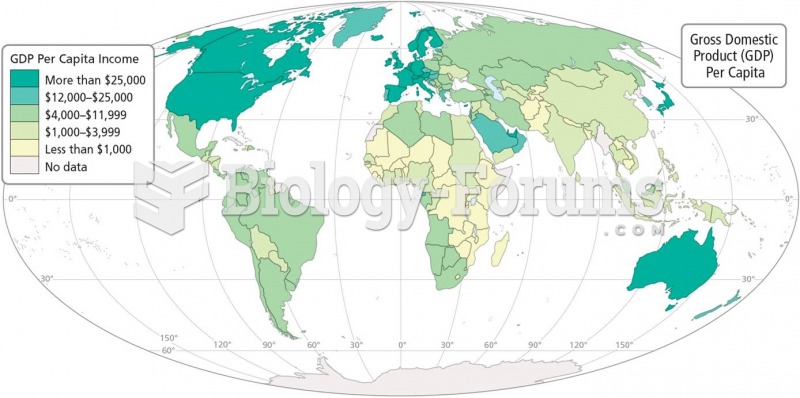
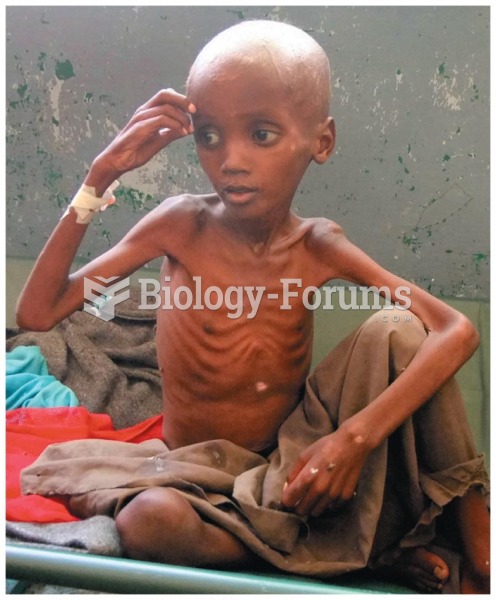
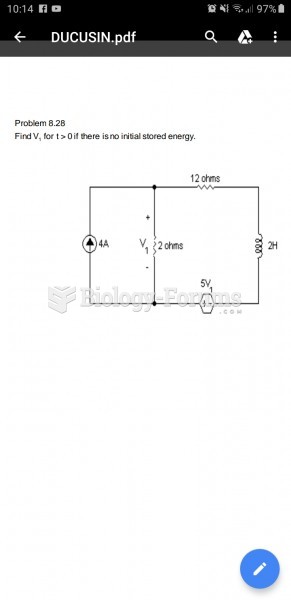
|
|
|
The first oral chemotherapy drug for colon cancer was approved by FDA in 2001.
In 2006, a generic antinausea drug named ondansetron was approved. It is used to stop nausea and vomiting associated with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
Glaucoma is a leading cause of blindness. As of yet, there is no cure. Everyone is at risk, and there may be no warning signs. It is six to eight times more common in African Americans than in whites. The best and most effective way to detect glaucoma is to receive a dilated eye examination.
Chronic marijuana use can damage the white blood cells and reduce the immune system's ability to respond to disease by as much as 40%. Without a strong immune system, the body is vulnerable to all kinds of degenerative and infectious diseases.