Answer to Question 1
Correct Answer: 1
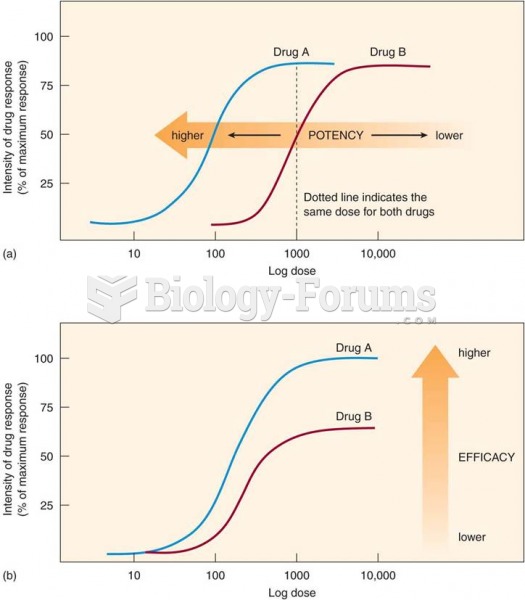
Rationale 1: Efficacy refers to the magnitude of maximal response that can be produced by a particular drug.
Rationale 2: Even though a drug is efficacious for a condition, it can still have side effects.
Rationale 3: Low potency does not guarantee a drug will not produce side effects.
Rationale 4: High-potency drugs do not necessarily provide the best response in the patient.
Global Rationale: Efficacy refers to the magnitude of maximal response that can be produced by a particular drug. Even though a drug is efficacious for a condition, it can still have side effects. Low potency does not guarantee a drug will not produce side effects. High-potency drugs do not necessarily provide the best response in the patient.
Answer to Question 2
Correct Answer: 2,4
Rationale 1: A higher dose of a potent drug may cause more serious adverse effects without greater efficacy.
Rationale 2: Efficacy is more important than potency in providing blood pressure control.
Rationale 3: This is not an appropriate response by the nurse.
Rationale 4: Efficacy is more important than potency in pharmacologic treatment.
Rationale 5: This is not an appropriate response, and the nurse cannot assume the order was supposed to be for two drugs.
Global Rationale: Efficacy is more important than potency in providing blood pressure control. Efficacy is more important than potency in pharmacologic treatment. A higher dose of a potent drug may cause more serious adverse effects without greater efficacy. Telling the client that the prescriber made an error is not an appropriate response by the nurse. The nurse cannot assume the order was supposed to be for two drugs.