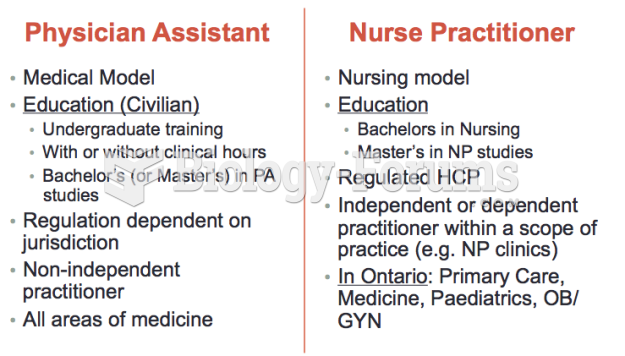
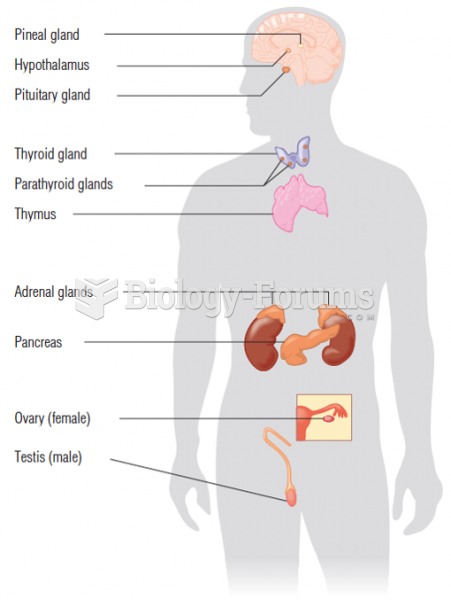
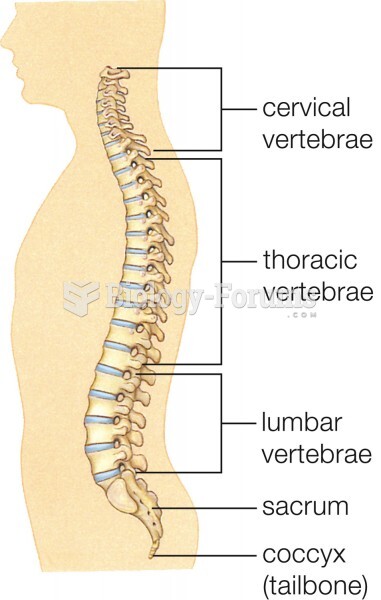
|
|
|
Though Candida and Aspergillus species are the most common fungal pathogens causing invasive fungal disease in the immunocompromised, infections due to previously uncommon hyaline and dematiaceous filamentous fungi are occurring more often today. Rare fungal infections, once accurately diagnosed, may require surgical debridement, immunotherapy, and newer antifungals used singly or in combination with older antifungals, on a case-by-case basis.
Cocaine was isolated in 1860 and first used as a local anesthetic in 1884. Its first clinical use was by Sigmund Freud to wean a patient from morphine addiction. The fictional character Sherlock Holmes was supposed to be addicted to cocaine by injection.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
Although not all of the following muscle groups are commonly used, intramuscular injections may be given into the abdominals, biceps, calves, deltoids, gluteals, laterals, pectorals, quadriceps, trapezoids, and triceps.
The longest a person has survived after a heart transplant is 24 years.