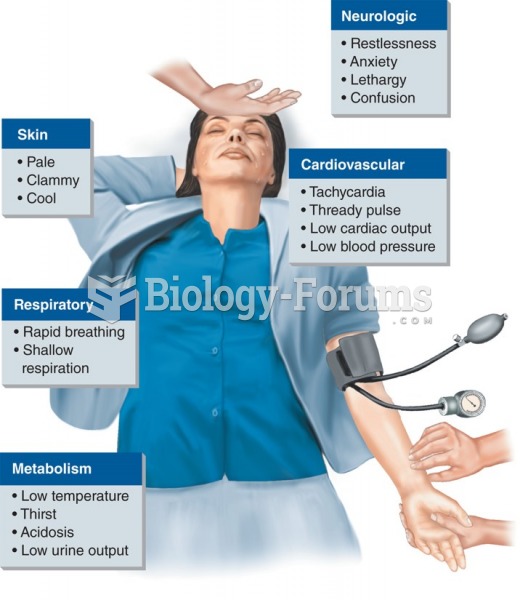
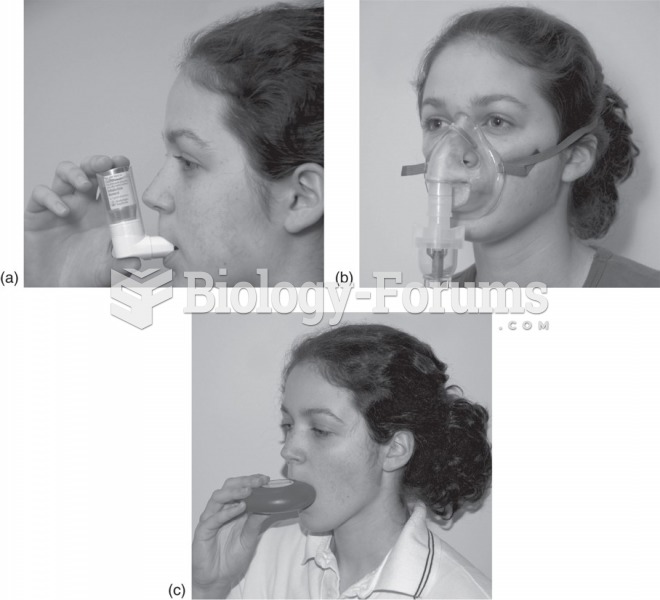
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Individuals are never “cured” of addictions. Instead, they learn how to manage their disease to lead healthy, balanced lives.
Did you know?
Multiple sclerosis is a condition wherein the body's nervous system is weakened by an autoimmune reaction that attacks the myelin sheaths of neurons.
Did you know?
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Did you know?
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
Did you know?
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.