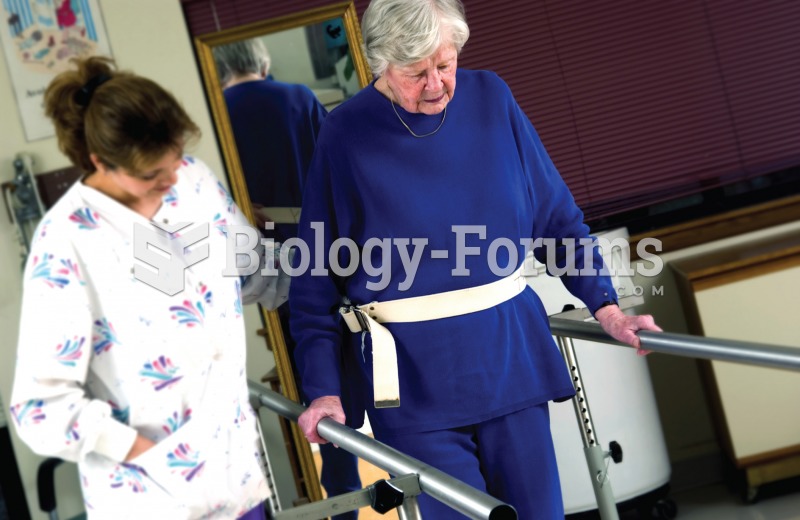
|
|
|
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Urine turns bright yellow if larger than normal amounts of certain substances are consumed; one of these substances is asparagus.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.