Answer to Question 1
C
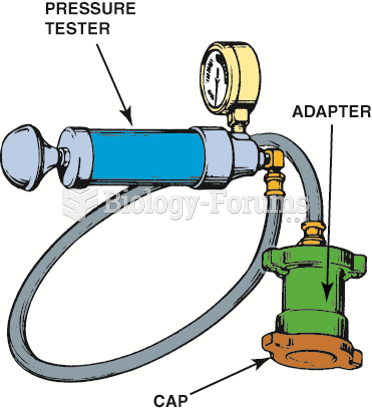
C. Presence of necrotic tissue (eschar, fibrin slough), debris, or other particulate matter requires high-pressure cleansing.
A. Presence of granulation tissue or new epithelial cells requires low-pressure wound cleansing.
B. Presence of minimum serosanguineous exudate requires low-pressure wound cleansing.
D. Presence of minimum residue from wound care products requires low-pressure wound cleansing.
Answer to Question 2
A
In addition to standard precautions, use contact precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses easily transmitted by direct patient contact or by contact with items in the patient's environment. Examples of such illnesses include gastrointestinal, respiratory, skin, or wound infection and colonization with multidrug-resistant bacteria judged by the infection control program as follows: (1) enteric with a low infectious dose or prolonged environmental survival, including Clostridium difficile, Escherichia coli, Shigella, hepatitis A, or rotavirus; or (2) skin infections that are highly contagious or that may occur on dry skin. Standard precautions apply to blood, all body fluids, secretions, excretions, nonintact skin, and mucous membranes. Patients who may be infected by pathogens that can be spread through direct patient contact may need more. The patient is not exhibiting signs of infection/colonization by pathogens that can be spread via the airborne route. In addition to standard precautions, use airborne precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses transmitted by airborne droplet nuclei. Examples of such illnesses include measles, varicella, and TB. The patient is not exhibiting signs of infection/colonization by pathogens that can be spread via large particle droplets. In addition to standard precautions, use droplet precautions for patients known or suspected to have serious illnesses transmitted by large particle droplets. Examples of such illnesses include invasive Haemophilus influenzae type b disease, pertussis, pneumonic plague, streptococcal pharyngitis, pneumonia, and scarlet fever in infants and young children, as well as mumps, parvovirus B19, and rubella.