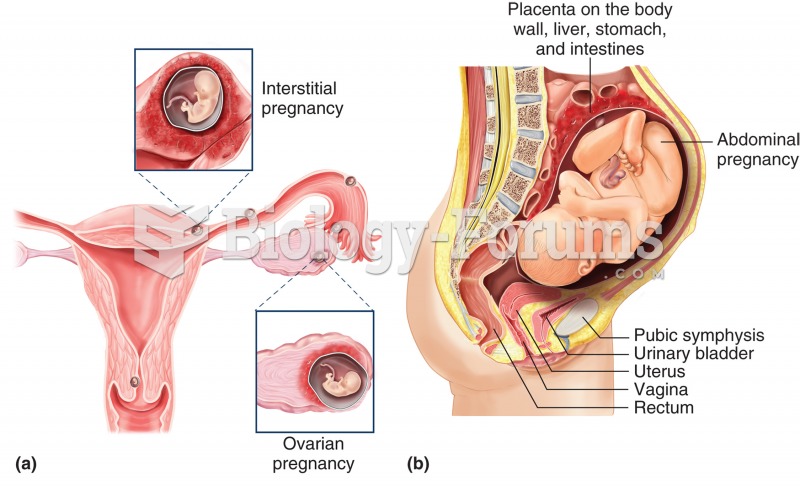
|
|
|
As of mid-2016, 18.2 million people were receiving advanced retroviral therapy (ART) worldwide. This represents between 43–50% of the 34–39.8 million people living with HIV.
In 1885, the Lloyd Manufacturing Company of Albany, New York, promoted and sold "Cocaine Toothache Drops" at 15 cents per bottle! In 1914, the Harrison Narcotic Act brought the sale and distribution of this drug under federal control.
According to animal studies, the typical American diet is damaging to the liver and may result in allergies, low energy, digestive problems, and a lack of ability to detoxify harmful substances.
The Babylonians wrote numbers in a system that used 60 as the base value rather than the number 10. They did not have a symbol for "zero."
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.