|
|
|
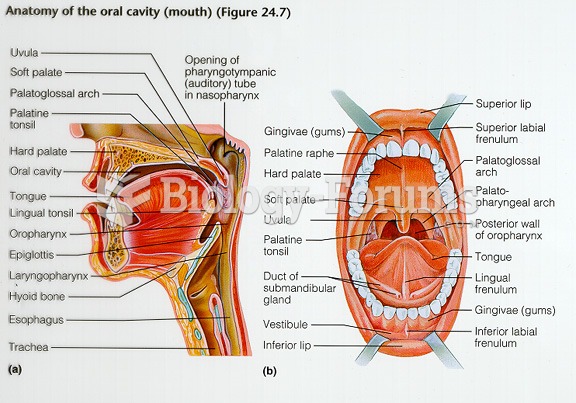
During pregnancy, a woman is more likely to experience bleeding gums and nosebleeds caused by hormonal changes that increase blood flow to the mouth and nose.
Women are two-thirds more likely than men to develop irritable bowel syndrome. This may be attributable to hormonal changes related to their menstrual cycles.
In 2010, opiate painkllers, such as morphine, OxyContin®, and Vicodin®, were tied to almost 60% of drug overdose deaths.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis syndrome are life-threatening reactions that can result in death. Complications include permanent blindness, dry-eye syndrome, lung damage, photophobia, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, permanent loss of nail beds, scarring of mucous membranes, arthritis, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Many patients' pores scar shut, causing them to retain heat.
Many supplement containers do not even contain what their labels say. There are many documented reports of products containing much less, or more, that what is listed on their labels. They may also contain undisclosed prescription drugs and even contaminants.