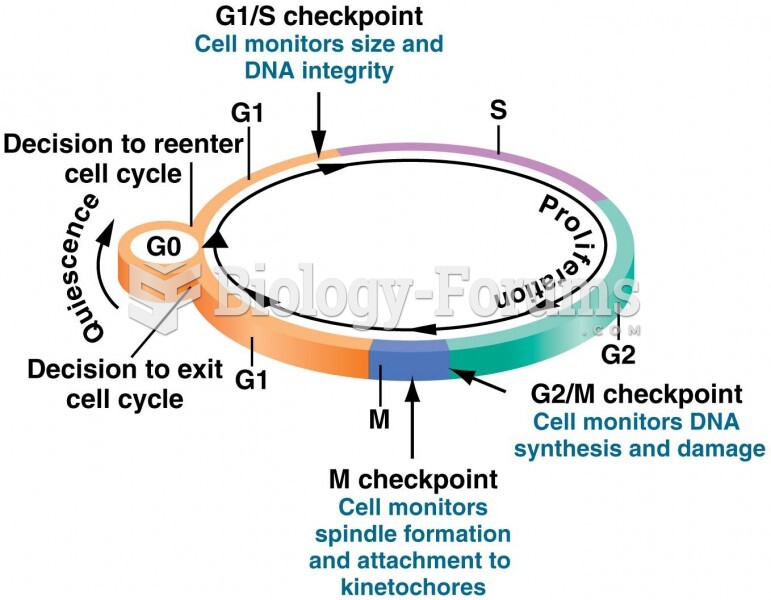
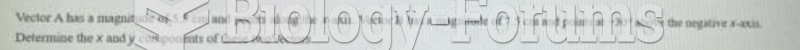|
|
|
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
Congestive heart failure is a serious disorder that carries a reduced life expectancy. Heart failure is usually a chronic illness, and it may worsen with infection or other physical stressors.
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Throughout history, plants containing cardiac steroids have been used as heart drugs and as poisons (e.g., in arrows used in combat), emetics, and diuretics.
Eat fiber! A diet high in fiber can help lower cholesterol levels by as much as 10%.
 On the slopes of Chimborazo, a 6,310 m high volcanic peak in the Andes Mountains of Ecuador, Alexand
On the slopes of Chimborazo, a 6,310 m high volcanic peak in the Andes Mountains of Ecuador, Alexand
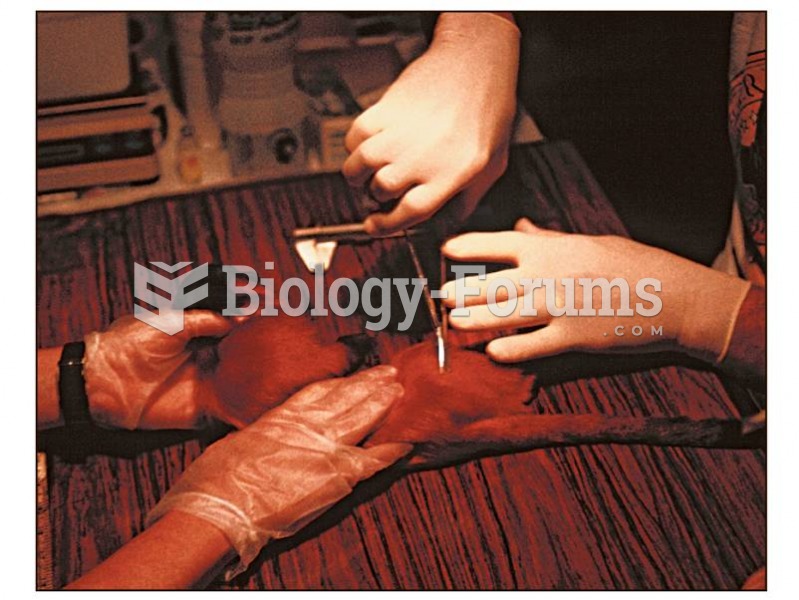 Modern primate study sometimes involves high-tech methods. This golden lion tamarin is having a batt
Modern primate study sometimes involves high-tech methods. This golden lion tamarin is having a batt
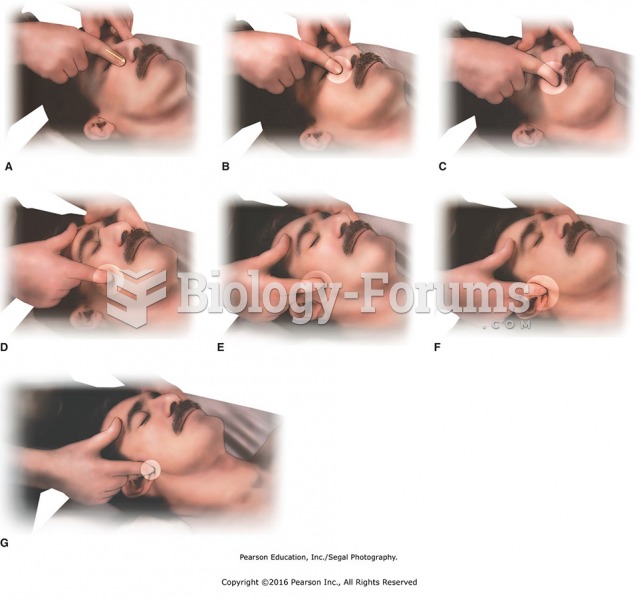 (A) Thumb slide down nose to (B) St-2. Press points along the cheekbone: (C) LI-20, (D) St-3, (E) ...
(A) Thumb slide down nose to (B) St-2. Press points along the cheekbone: (C) LI-20, (D) St-3, (E) ...