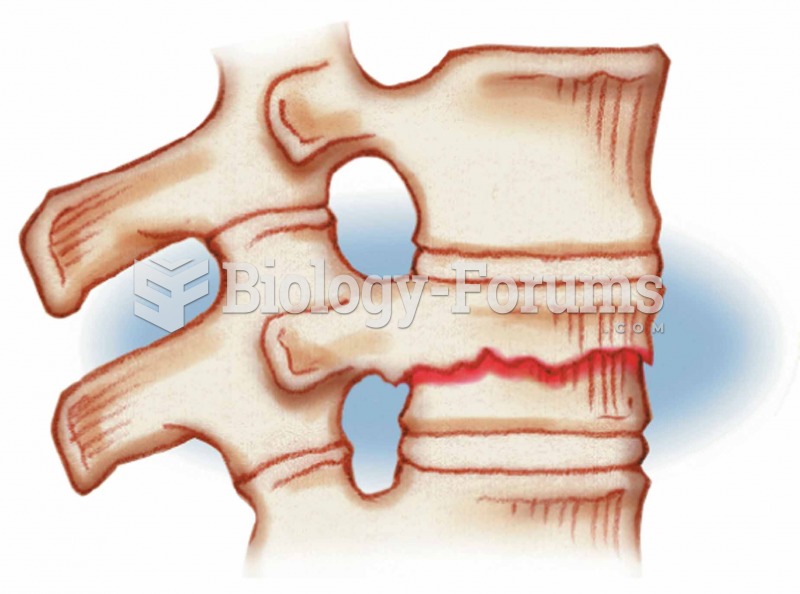
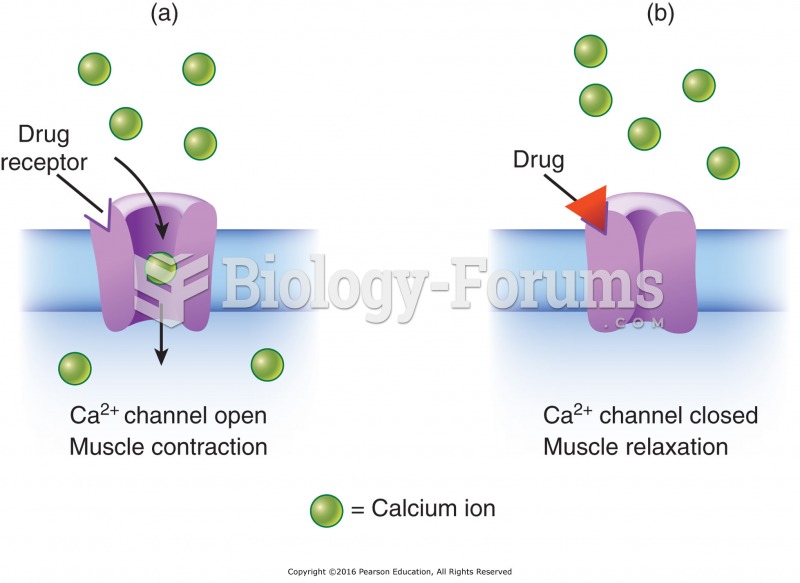
|
|
|
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Vaccines cause herd immunity. If the majority of people in a community have been vaccinated against a disease, an unvaccinated person is less likely to get the disease since others are less likely to become sick from it and spread the disease.
Signs and symptoms of a drug overdose include losing consciousness, fever or sweating, breathing problems, abnormal pulse, and changes in skin color.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.