|
|
|
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
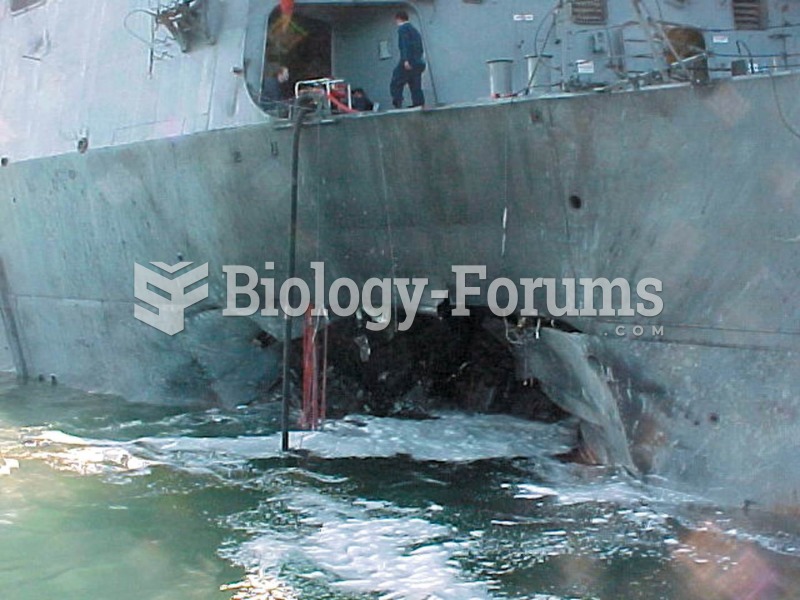
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
Dogs have been used in studies to detect various cancers in human subjects. They have been trained to sniff breath samples from humans that were collected by having them breathe into special tubes. These people included 55 lung cancer patients, 31 breast cancer patients, and 83 cancer-free patients. The dogs detected 54 of the 55 lung cancer patients as having cancer, detected 28 of the 31 breast cancer patients, and gave only three false-positive results (detecting cancer in people who didn't have it).
For high blood pressure (hypertension), a new class of drug, called a vasopeptidase blocker (inhibitor), has been developed. It decreases blood pressure by simultaneously dilating the peripheral arteries and increasing the body's loss of salt.