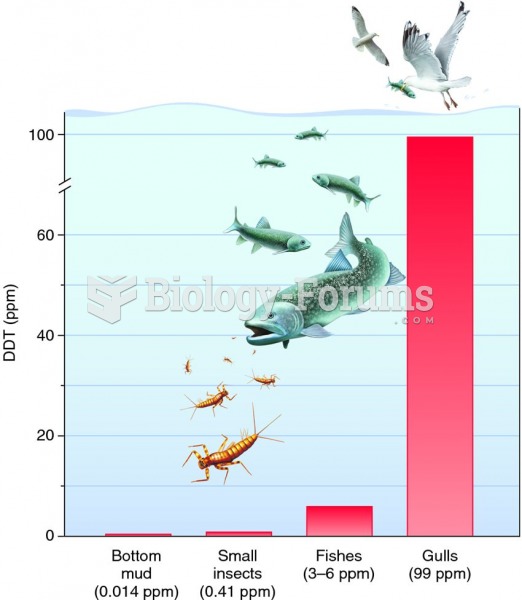
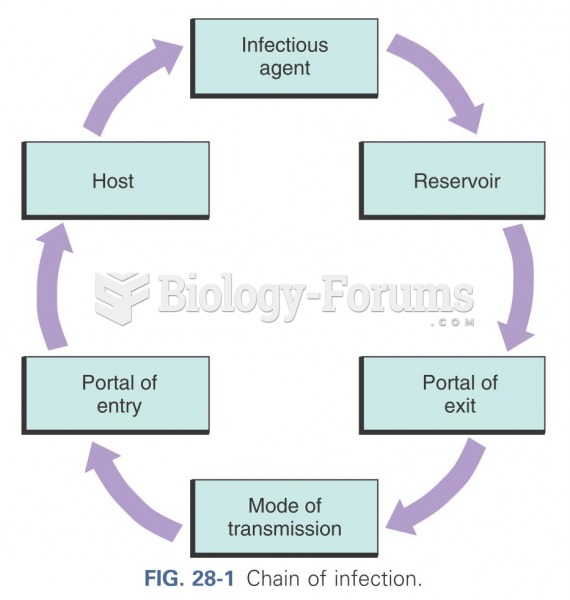
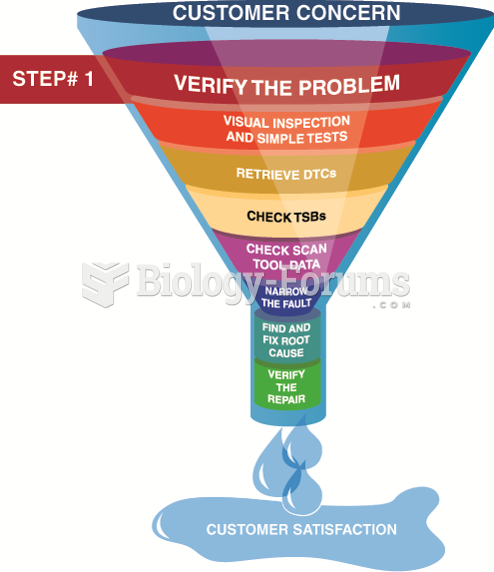
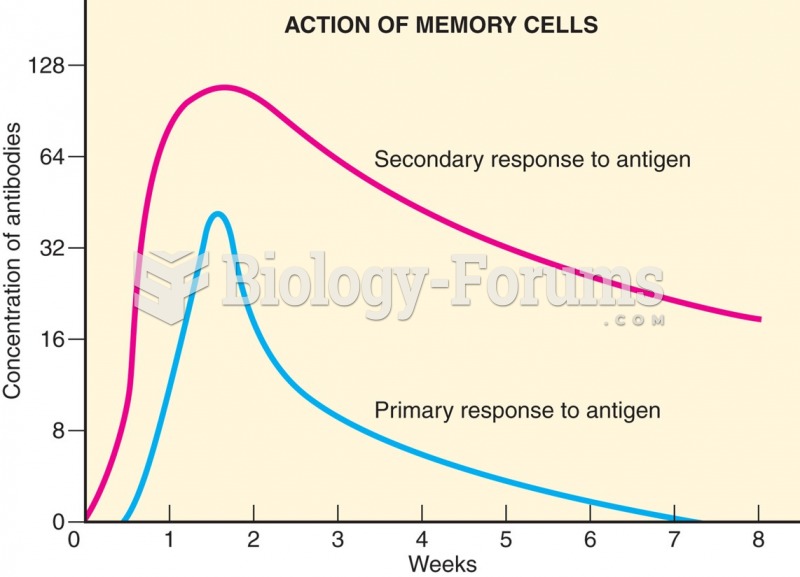
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Elderly adults are living longer, and causes of death are shifting. At the same time, autopsy rates are at or near their lowest in history.
Did you know?
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Did you know?
Persons who overdose with cardiac glycosides have a better chance of overall survival if they can survive the first 24 hours after the overdose.
Did you know?
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
Did you know?
Pubic lice (crabs) are usually spread through sexual contact. You cannot catch them by using a public toilet.